Overexpression of eCLCA1 in small airways of horses with recurrent airway obstruction
- PMID: 15879574
- PMCID: PMC1383431
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.4A6599.2005
Overexpression of eCLCA1 in small airways of horses with recurrent airway obstruction
Abstract
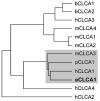
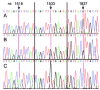
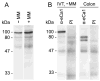
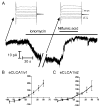
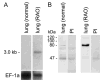
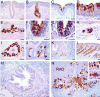
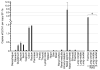
The human hCLCA1 and murine mCLCA3 (chloride channels, calcium-activated) have recently been identified as promising therapeutic targets in asthma. Recurrent airway obstruction in horses is an important animal model of human asthma. Here, we have cloned and characterized the first equine CLCA family member, eCLCA1. The 913 amino acids eCLCA1 polypeptide forms a 120-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein that is processed to an 80-kDa protein in vivo. Three single nucleotide polymorphisms were detected in the eCLCA1 coding region in 14 horses, resulting in two amino acid changes (485H/R and 490V/L). However, no functional differences were recorded between the channel properties of the two variants in transfected HEK293 cells. The eCLCA1 protein was detected immunohistochemically in mucin-producing cells in the respiratory and intestinal tracts, cutaneous sweat glands, and renal mucous glands. Strong overexpression of eCLCA1 was observed in the airways of horses with recurrent airway obstruction using Northern blot hybridization, Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and real-time quantitative RT-PCR. The results suggest that spontaneous or experimental recurrent airway obstruction in horses may serve as a model to study the role of CLCA homologs in chronic airway disease with overproduction of mucins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of CLCA proteins in inflammatory airway disease.Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:425-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163253. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18954282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A soluble secreted glycoprotein (eCLCA1) is overexpressed due to goblet cell hyperplasia and metaplasia in horses with recurrent airway obstruction.Vet Pathol. 2007 Nov;44(6):901-11. doi: 10.1354/vp.44-6-901. Vet Pathol. 2007. PMID: 18039903
-
Increased mucus accumulation in horses chronically affected with recurrent airway obstruction is not associated with up-regulation of CLCA1, EGFR, MUC5AC, Bcl-2, IL-13 and INF-gamma expression.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008 Sep 15;125(1-2):8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.05.011. Epub 2008 May 23. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008. PMID: 18597857
-
hCLCA1 DNA vaccine suppresses cell hyperplasia and mucin expression of goblet cells in vitro.Respiration. 2013;86(6):486-96. doi: 10.1159/000354180. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Respiration. 2013. PMID: 24021422
-
Structure and function of CLCA proteins.Physiol Rev. 2005 Jul;85(3):1061-92. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2004. Physiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15987802 Review.
Cited by
-
Murine mCLCA5 is expressed in granular layer keratinocytes of stratified epithelia.Histochem Cell Biol. 2010 Mar;133(3):285-99. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0667-0. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20012443
-
Differential expression of calcium-activated chloride channels (CLCA) gene family members in the small intestine of cystic fibrosis mouse models.Histochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;126(2):239-50. doi: 10.1007/s00418-006-0164-7. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16514548
-
Self-cleavage of human CLCA1 protein by a novel internal metalloprotease domain controls calcium-activated chloride channel activation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 7;287(50):42138-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410282. Epub 2012 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23112050 Free PMC article.
-
The porcine chloride channel calcium-activated family member pCLCA4a mirrors lung expression of the human hCLCA4.J Histochem Cytochem. 2012 Jan;60(1):45-56. doi: 10.1369/0022155411426455. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012. PMID: 22205680 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CLCA proteins in inflammatory airway disease.Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:425-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163253. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18954282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banks W (1993) Applied Veterinary Histology. 3rd ed. St Louis, Mosby Year Book
-
- Bice DE, Seagrave J, Green FH. Animal models of asthma: potential usefulness for studying health effects of inhaled particles. Inhal Toxicol. 2000;12:829–862. - PubMed
-
- Davis E, Rush BR. Equine recurrent airway obstruction: pathogenesis, diagnosis and patient management. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2002;18:453–467. - PubMed
-
- Dellmann HD, Eurell J (1998) Textbook of Veterinary Histology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
-
- Fuller CM, Ji HL, Tousson A, Elble RC, Pauli BU, Benos DJ. Ca(2+)-activated Cl(−) channels: a newly emerging anion transport family. Pflugers Arch. 2001;443(suppl 1):S107–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

