Binding and repression of translation of the cognate mRNA by Trichinella spiralis thymidylate synthase differ from the corresponding interactions of the human enzyme
- PMID: 15882146
- PMCID: PMC1199661
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050548
Binding and repression of translation of the cognate mRNA by Trichinella spiralis thymidylate synthase differ from the corresponding interactions of the human enzyme
Retraction in
-
Binding and repression of translation of the cognate mRNA by Trichinella spiralis thymidylate synthase differ from the corresponding interactions of the human enzyme.Biochem J. 2007 Mar 15;402(3):601. doi: 10.1042/bj4020601. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17326266 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
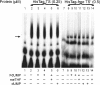
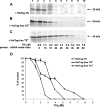
Thymidylate synthase (TS) of Trichinella spiralis, a parasitic nematode causing trichinellosis, was found to bind its own mRNA and repress translation of the latter, similar to its human counter-part [Chu, Koeller, Casey, Drake, Chabner, Elwood, Zinn and Allegra (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8977-8981]. However, in striking contrast with human TS, the parasite enzyme's interaction with mRNA was not affected by any of the substrate (deoxyuridylate or N(5,10)-methylenetetrahydrofolate) nor by the inhibitor (fluorodeoxyuridylate; used alone or in the presence of N(5,10)-methylenetetrahydrofolate) similar to that shown for the bifunctional enzyme from Plasmodium falciparum [Zhang and Rathod (2002) Science 296, 545-547]. Moreover, repression of the translation of the parasite enzyme was enhanced by the same ligands that were shown by others (Chu et al., 1991) to prevent human TS from impairing its translation. On comparing the capacity of TS to bind to its cognate mRNA, relative to its ability to inhibit its translation, the same enzyme preparation was active as translational repressor at a considerably lower protein/mRNA ratio, suggesting the two phenomena to be disconnected. Of interest is the fact that the presence of the enzyme protein N-terminal methionine proved to be critical for binding, but not for repression of its translation, indicating that mRNA binding requires a methionine or an adduct (i.e. methionine-histidine) at the N-terminus of TS, but that the translational repression effect does not. Notably, chicken liver dihydrofolate reductase, which is incapable of binding to T. spiralis TS mRNA, repressed the translation of TS.
Figures

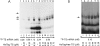
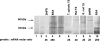

Similar articles
-
Trichinella spiralis thymidylate synthase: cDNA cloning and sequencing, and developmental pattern of mRNA expression.Parasitology. 2004 Feb;128(Pt 2):209-21. doi: 10.1017/s0031182003004426. Parasitology. 2004. PMID: 15030008
-
Repression of human thymidylate synthase mRNA translation by antisense 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotides.Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1998 Oct;8(5):371-8. doi: 10.1089/oli.1.1998.8.371. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1998. PMID: 9826264
-
Autoregulation of human thymidylate synthase messenger RNA translation by thymidylate synthase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8977-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8977. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. PMID: 1924359 Free PMC article.
-
The role of thymidylate synthase as an RNA binding protein.Bioessays. 1996 Mar;18(3):191-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180306. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8867733 Review.
-
Thymidylate synthase as a translational regulator of cellular gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):174-82. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00080-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084459 Review.
Cited by
-
Variants of human thymidylate synthase with loop 181-197 stabilized in the inactive conformation.Protein Sci. 2009 Aug;18(8):1628-36. doi: 10.1002/pro.171. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19569192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carreras C. W., Santi D. The catalytic mechanism and structure of thymidylate synthase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995;64:721–762. - PubMed
-
- Danenberg P. V. Thymidylate synthetase – a target enzyme in cancer chemotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1977;473:73–97. - PubMed
-
- Hardy L. W., Finer-Moore J. S., Montfort W. R., Jones M. O., Santi D. V., Stroud R. M. Atomic structure of thymidylate synthase: target for rational drug design. Science. 1987;235:448–455. - PubMed
-
- Shoichet B. K., Stroud R. M., Santi D. V., Kuntz I. D., Perry K. M. Structure-based discovery of inhibitors of thymidylate synthase. Science. 1993;259:1445–1450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

