Generation of hematopoietic repopulating cells from human embryonic stem cells independent of ectopic HOXB4 expression
- PMID: 15883170
- PMCID: PMC2212922
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041888
Generation of hematopoietic repopulating cells from human embryonic stem cells independent of ectopic HOXB4 expression
Abstract
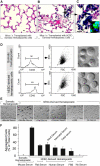
Despite the need for alternative sources of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), the functional capacity of hematopoietic cells generated from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) has yet to be evaluated and compared with adult sources. Here, we report that somatic and hESC-derived hematopoietic cells have similar phenotype and in vitro clonogenic progenitor activity. However, in contrast with somatic cells, hESC-derived hematopoietic cells failed to reconstitute intravenously transplanted recipient mice because of cellular aggregation causing fatal emboli formation. Direct femoral injection allowed recipient survival and resulted in multilineage hematopoietic repopulation, providing direct evidence of HSC function. However, hESC-derived HSCs had limited proliferative and migratory capacity compared with somatic HSCs that correlated with a distinct gene expression pattern of hESC-derived hematopoietic cells that included homeobox (HOX) A and B gene clusters. Ectopic expression of HOXB4 had no effect on repopulating capacity of hESC-derived cells. We suggest that limitations in the ability of hESC-derived HSCs to activate a molecular program similar to somatic HSCs may contribute to their atypical in vivo behavior. Our study demonstrates that HSCs can be derived from hESCs and provides an in vivo system and molecular foundation to evaluate strategies for the generation of clinically transplantable HSC from hESC lines.
Figures


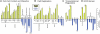

Similar articles
-
Hematopoietic development from human embryonic stem cell lines.Exp Hematol. 2005 Sep;33(9):987-96. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2005.06.002. Exp Hematol. 2005. PMID: 16140146 Review.
-
Enforced activation of STAT5A facilitates the generation of embryonic stem-derived hematopoietic stem cells that contribute to hematopoiesis in vivo.Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1191-204. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2004-0033. Stem Cells. 2004. PMID: 15579639
-
Forced expression of HoxB4 enhances hematopoietic differentiation by human embryonic stem cells.Mol Cells. 2008 Jun 30;25(4):487-93. Epub 2008 May 29. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18511880
-
Recombinant HoxB4 fusion proteins enhance hematopoietic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2007 Aug;16(4):547-59. doi: 10.1089/scd.2007.0002. Stem Cells Dev. 2007. PMID: 17784829
-
Hematopoietic development from human embryonic stem cells.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007:11-6. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2007.1.11. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007. PMID: 18024603 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of E-cadherin and other cell adhesion molecules in survival and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Jan-Feb;6(1):59-70. doi: 10.4161/cam.19583. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22647941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell therapy: an exercise in patience and prudence.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Jan 5;368(1609):20110334. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0334. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23166396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoiesis from pluripotent stem cell lines.Int J Hematol. 2010 Apr;91(3):384-91. doi: 10.1007/s12185-010-0519-7. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Int J Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20169427 Review.
-
Designer blood: creating hematopoietic lineages from embryonic stem cells.Blood. 2006 Feb 15;107(4):1265-75. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-3621. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16254136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Derivation of normal macrophages from human embryonic stem (hES) cells for applications in HIV gene therapy.Retrovirology. 2006 Apr 19;3:24. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-24. Retrovirology. 2006. PMID: 16623949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siena, S., M. Bregni, B. Brando, N. Belli, F. Ravagnani, L. Gandola, A.C. Stern, P.M. Lansdorp, G. Bonadonna, and A.M. Gianni. 1991. Flow cytometry for clinical estimation of circulating hematopoietic progenitors for autologous transplantation in cancer patients. Blood. 77:400–409. - PubMed
-
- Heimfeld, S. 2003. HLA-identical stem cell transplantation: is there an optimal CD34 cell dose? Bone Marrow Transplant. 31:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Wang, L., L. Li, F. Shojaei, P. Menendez, T. Martin, A. Rouleau, and M. Bhatia. 2004. Endothelial and hematopoietic cell fate of human embryonic stem cells originates from primitive endothelium with hemangioblastic properties. Immunity. 21:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Wang, J.C., C. Dorrell, C.Y. Ito, T. Inamitsu, G. Guenechea, O.I. Gan, and J.E. Dick. 2001. Normal and leukemic human stem cells assayed in immune-deficient mice. In Hematopoiesis: A Developmental Approach. L.I. Zon, editor. Oxford University Press, New York. 99–118.
-
- Perrault, C., N. Ajzenberg, P. Legendre, G. Rastegar-Lari, D. Meyer, J.A. Lopez, and D. Baruch. 1999. Modulation by heparin of the interaction of the A1 domain of von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 94:4186–4194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

