Spatial distribution and functional significance of activated vinculin in living cells
- PMID: 15883197
- PMCID: PMC2171941
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200410100
Spatial distribution and functional significance of activated vinculin in living cells
Abstract
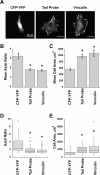
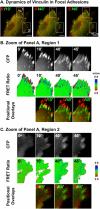
Conformational change is believed to be important to vinculin's function at sites of cell adhesion. However, nothing is known about vinculin's conformation in living cells. Using a Forster resonance energy transfer probe that reports on changes in vinculin's conformation, we find that vinculin is in the actin-binding conformation in a peripheral band of adhesive puncta in spreading cells. However, in fully spread cells with established polarity, vinculin's conformation is variable at focal adhesions. Time-lapse imaging reveals a gradient of conformational change that precedes loss of vinculin from focal adhesions in retracting regions. At stable or protruding regions, recruitment of vinculin is not necessarily coupled to the actin-binding conformation. However, a different measure of vinculin conformation, the recruitment of vinexin beta by activated vinculin, shows that autoinhibition of endogenous vinculin is relaxed at focal adhesions. Beyond providing direct evidence that vinculin is activated at focal adhesions, this study shows that the specific functional conformation correlates with regional cellular dynamics.
Figures







Similar articles
-
New insights into vinculin function and regulation.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;287:191-231. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386043-9.00005-0. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21414589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Raver1 interactions with vinculin and RNA suggest a feed-forward pathway in directing mRNA to focal adhesions.Structure. 2009 Jun 10;17(6):833-42. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.04.010. Structure. 2009. PMID: 19523901 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of vinculin activation and nanoscale spatial organization in focal adhesions.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;17(7):880-92. doi: 10.1038/ncb3180. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26053221 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of substrate stiffness and actomyosin contractility on coupling between force transmission and vinculin-paxillin recruitment at single focal adhesions.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jul 7;28(14):1901-1911. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-02-0116. Epub 2017 May 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28468976 Free PMC article.
-
Vinculin and metavinculin: oligomerization and interactions with F-actin.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 17;587(8):1220-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.02.042. Epub 2013 Mar 1. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23466368 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlative light and electron microscopy reveals fork-shaped structures at actin entry sites of focal adhesions.Biol Open. 2022 Nov 1;11(11):bio059417. doi: 10.1242/bio.059417. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 36409550 Free PMC article.
-
Vinculin Force-Sensitive Dynamics at Focal Adhesions Enable Effective Directed Cell Migration.Biophys J. 2018 Apr 10;114(7):1680-1694. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.019. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29642037 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis and cellular functions of vinculin-actin directional catch bonding.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 14;14(1):8300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43779-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38097542 Free PMC article.
-
Actinidia chinensis polysaccharide interferes with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer by regulating the nuclear transcription factor-κB pathway to inhibit invasion and metastasis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Oct;44(5):896-905. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240806.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39380220 Free PMC article.
-
Vinculin motion modes analysis with elastic network model.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(1):208-20. doi: 10.3390/ijms13010208. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22312248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alenghat, F.J., B. Fabry, K.Y. Tsai, W.H. Goldmann, and D.E. Ingber. 2000. Analysis of cell mechanics in single vinculin-deficient cells using a magnetic tweezer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Bakolitsa, C., J.M. de Pereda, C.R. Bagshaw, D.R. Critchley, and R.C. Liddington. 1999. Crystal structure of the vinculin tail suggests a pathway for activation. Cell. 99:603–613. - PubMed
-
- Bakolitsa, C., D.M. Cohen, L.A. Bankston, A.A. Bobkov, G.W. Cadwell, L. Jennings, D.R. Critchley, S.W. Craig, and R.C. Liddington. 2004. Structural basis for vinculin activation at sites of cell adhesion. Nature. 430:583–586. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N.Q., U.S. Schwarz, D. Riveline, P. Goichberg, G. Tzur, I. Sabanay, D. Mahalu, S. Safran, A. Bershadsky, L. Addadi, and B. Geiger. 2001. Force and focal adhesion assembly: a close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

