Patellamide A and C biosynthesis by a microcin-like pathway in Prochloron didemni, the cyanobacterial symbiont of Lissoclinum patella
- PMID: 15883371
- PMCID: PMC1091749
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0501424102
Patellamide A and C biosynthesis by a microcin-like pathway in Prochloron didemni, the cyanobacterial symbiont of Lissoclinum patella
Abstract
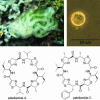
Prochloron spp. are obligate cyanobacterial symbionts of many didemnid family ascidians. It has been proposed that the cyclic peptides of the patellamide class found in didemnid extracts are synthesized by Prochloron spp., but studies in which host and symbiont cells are separated and chemically analyzed to identify the biosynthetic source have yielded inconclusive results. As part of the Prochloron didemni sequencing project, we identified patellamide biosynthetic genes and confirmed their function by heterologous expression of the whole pathway in Escherichia coli. The primary sequence of patellamides A and C is encoded on a single ORF that resembles a precursor peptide. We propose that this prepatellamide is heterocyclized to form thiazole and oxazoline rings, and the peptide is cleaved to yield the two cyclic patellamides, A and C. This work represents the full sequencing and functional expression of a marine natural-product pathway from an obligate symbiont. In addition, a related cluster was identified in Trichodesmium erythraeum IMS101, an important bloom-forming cyanobacterium.
Figures


References
-
- Newman, D. J. & Cragg, G. M. (2004) J. Nat. Prod. 67, 1216-1238. - PubMed
-
- Simmons, L. T., Andrianasolo, E., McPhail, K., Flatt, P. & Gerwick, W. H. (2005) Mol. Cancer Ther. 4, 333-342. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner, D. J., He, H. Y., Unson, M. D. & Bewley, C. A. (1993) Gazz. Chim. Ital. 123, 301-307.
-
- Kobayashi, J. & Ishibashi, M. (1993) Chem. Rev. (Washington, D.C.) 93, 1753-1770.
-
- Sings, H. L. & Rinehart, K. L. (1996) J. Ind. Microbiol. 17, 385-396.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

