Increased activity of Pgp multidrug transporter in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 15884110
- PMCID: PMC4305904
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2720
Increased activity of Pgp multidrug transporter in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether local antibiotic resistance involves P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-mediated active drug out-pumping during Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) infection treatment with classic antibiotic therapy.
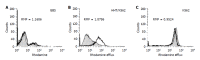
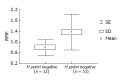
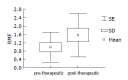
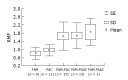
Methods: Pgp activity was determined in gastric mucosa biopsy specimens obtained from 53 patients with pathohistologically verified gastritis and microbiologically confirmed H pylori infection, and compared with the Pgp activity in 12 control subjects with normal endoscopic findings. The H pylori positive patients were treated with short-term 7-d therapy consisting of two antibiotics (amoxicillin and azithromycin/metronidazole and clarithromycin) and a proton pump inhibitor. Pgp activity was determined by flow cytometry in the test of rhodamine dye efflux and quantified as mean fluorescence ratio (RMF).
Results: Upon the first cycle, H pylori was successfully eradicated in 20 patients, whereas therapy was continued in 33 patients. In the course of antibiotic therapy, RMF increased (P<0.05) and gastric cells showed higher rhodamine dye efflux. The mean pre-treatment RMF values were also higher (P<0.0001) in patients with multiple therapeutic failure than in those with successful H pylori eradication and control subjects.
Conclusion: Pgp might be one of the causes of therapy failure in patients with H pylori and antibiotic therapy could be chosen and followed up on the basis of the Pgp transporter local activity.
Figures
References
-
- Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Hungin AP, Jones R, Axon A, Graham DY, Tytgat G. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection--the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Georgopoulos SD, Ladas SD, Karatapanis S, Mentis A, Spiliadi C, Artikis V, Raptis SA. Factors that may affect treatment outcome of triple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy with omeprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin. Dig Dis Sci. 2000;45:63–67. - PubMed
-
- Megraud F. Resistance of Helicobacter pylori. In: Scarpignato C, Bianchi Porro G, Volume eds. Clinical pharmacology and therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection. Prog Basic Clin Pharmacol. Basel: Karger. 1999;11:329–352.
-
- van der Hulst RWM, Tytgat GNJ. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori eradication failure. In: Scarpignato C, Bianchi Porro G, Volume eds, editors. Clinical pharmacology and therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection. Prog Basic Clin Pharmacol. Vol. 11. Basel: Karger; 1999. pp. 317–328.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

