How can colorectal neoplasms be treated during colonoscopy?
- PMID: 15884128
- PMCID: PMC4305922
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2806
How can colorectal neoplasms be treated during colonoscopy?
Abstract
Aim: For many physicians who ordinarily treat patients with colonic diseases, colonoscopy is considered a prime study interest. Developments in colonoscopic equipment and methods have led to a large number of endoscopic diagnoses and treatment for colorectal neoplasms. The purpose of this investigation is to evaluate the efficacy and outcomes of endoscopic treatment for colorectal neoplastic lesions.
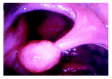
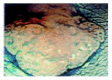
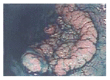
Methods: From September 1999 to May 2003, 11 447 consecutive colonoscopic examinations in 9864 patients were gathered; totaling 5502 endoscopic treatments for colorectal neoplasms. Macroscopic characteristics of the neoplasms were classified into protruded (n = 3 953), sessile (n = 1402), lateral spreading tumor (n = 139) and depressed lesions (n = 8). Snare polypectomy was conducted in 3984 lesions, hot forcep removal in 1368 lesions, and endoscopic mucosal resection in 150 lesions.
Results: Histological diagnoses were 4596 neoplastic lesions (4 376 adenomas and 220 adenocarcinomas) and 906 non-neoplastic lesions (891 hyperplastic and 15 inflammatory polyps). For the adenocarcinoma group, 31 instances involved submucosal invasion or resection margin, who received further operations, while 13 surgical specimens discovered no residual tumors. Three perforations and 96 bleedings were found following endoscopic treatment. No procedure-related mortality was found and no recurrent malignancy was found after 14-56 mo follow-up.
Conclusion: To lower the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer, endoscopic treatment for colorectal neoplasms is a simple and safe procedure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treating colorectal polypoid neoplasms during a colonoscopy.Chang Gung Med J. 2005 Nov;28(11):801-7. Chang Gung Med J. 2005. PMID: 16422187
-
Endoscopic treatment of colorectal neoplasms: a simple and safe procedure to lower the incidence of colorectal cancers.Dig Dis Sci. 2008 May;53(5):1297-302. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0236-8. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18363105
-
Outcomes of EMR of defiant colorectal lesions directed to an endoscopy referral center.Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Aug;76(2):255-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.02.060. Epub 2012 May 31. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22657404
-
Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of early colorectal cancer.World J Surg. 1997 Sep;21(7):694-701. doi: 10.1007/s002689900293. World J Surg. 1997. PMID: 9276699 Review.
-
Laterally spreading tumors in the colon and rectum.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Oct;24(10):1123-34. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328355e2d9. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22732357 Review.
Cited by
-
Colonoscopic polypectomy: a critical review of recent literature.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2006 Oct;8(5):430-3. doi: 10.1007/s11894-006-0030-8. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2006. PMID: 16968612 Review.
References
-
- Kawamura YJ, Sugamata Y, Yoshino K, Abo Y, Nara S, Sumita T, Setoyama R, Kiribuchi Y, Kawano N. Endoscopic resection for submucosally invasive colorectal cancer: is it feasible? Surg Endosc. 1999;13:224–227. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura K, Taniguchi H, Yamaguchi T, Sawai K, Takahashi T. Clinical outcome of surgical treatment for invasive early colorectal cancer in Japan. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997;44:108–115. - PubMed
-
- Kudo S, Kashida H, Nakajima T, Tamura S, Nakajo K. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of early colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 1997;21:694–701. - PubMed
-
- Kudo S. Endoscopic mucosal resection of flat and depressed types of early colorectal cancer. Endoscopy. 1993;25:455–461. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical