Monoclonal antibodies to SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV): identification of neutralizing and antibodies reactive to S, N, M and E viral proteins
- PMID: 15885812
- PMCID: PMC7112802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.03.021
Monoclonal antibodies to SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV): identification of neutralizing and antibodies reactive to S, N, M and E viral proteins
Abstract
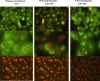
Monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) against the Urbani strain of the SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) were developed and characterized for reactivity to SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV S, N, M, and E proteins using enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent (ELISA), radioimmunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, Western Blot and microneutralization assays. Twenty-six mAbs were reactive to SARS-CoV by ELISA, and nine were chosen for detailed characterization. Five mAbs reacted against the S protein, two against the M protein, and one each against the N and E proteins. Two of five S protein mAbs neutralized SARS-CoV infection of Vero E6 cells and reacted to an epitope within amino acids 490-510 in the S protein. While two of the three non-neutralizing antibodies recognized at second epitope within amino acids 270-350. The mAbs characterized should prove useful for developing SARS-CoV diagnostic assays and for studying the biology of infection and pathogenesis of disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular and biological characterization of human monoclonal antibodies binding to the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1635-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1635-1644.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650189 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope mapping and biological function analysis of antibodies produced by immunization of mice with an inactivated Chinese isolate of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV).Virology. 2005 Mar 30;334(1):134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.01.035. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15749129 Free PMC article.
-
SARS patients-derived human recombinant antibodies to S and M proteins efficiently neutralize SARS-coronavirus infectivity.Biomed Environ Sci. 2005 Dec;18(6):363-74. Biomed Environ Sci. 2005. PMID: 16544518
-
Neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus: target, mechanism of action, and therapeutic potential.Rev Med Virol. 2012 Jan;22(1):2-17. doi: 10.1002/rmv.706. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Rev Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 21905149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overall picture of SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) genome-encoded major proteins: structures, functions and drug development.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(35):4539-53. doi: 10.2174/138161206779010459. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 17168760 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibody-mediated synergy and interference in the neutralization of SARS-CoV at an epitope cluster on the spike protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Dec 18;390(3):1056-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.115. Epub 2009 Oct 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19861118 Free PMC article.
-
Fully human monoclonal antibody directed to proteolytic cleavage site in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus S protein neutralizes the virus in a rhesus macaque SARS model.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 1;203(11):1574-81. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir084. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21592986 Free PMC article.
-
Current vaccine technology with an emphasis on recombinant measles virus as a new perspective for vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.EuroMediterr J Environ Integr. 2021;6(2):61. doi: 10.1007/s41207-021-00263-6. Epub 2021 Jul 4. EuroMediterr J Environ Integr. 2021. PMID: 34250222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): a systematic review for potential vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Dec 31;18(1):1865774. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1865774. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 33545014 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting potential druggable targets against SARS-CoV-2 and repurposing therapeutics under preclinical study and clinical trials: A comprehensive review.Drug Dev Res. 2020 Dec;81(8):919-941. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21709. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Drug Dev Res. 2020. PMID: 32632960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berry J.D., Jones S., Drebot M.A., Andonov A., Sabara M., Yuan X.Y., Weingartl H., Fernando L., Marszal P., Gren J., Nicolas B., Andonova M., Ranada F., Gubbins M.J., Blake Ball T., Kitching P., Li Y., Kabani A., Plummer F. Development and characterization of neutralising monoclonal antibody to the SARS-coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods. 2004;120:87–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Che X.Y., Hao W., Qiu L.W., Pan Y.X., Liao Z.Y., Xu H., Chen J.J., Hou J.L., Woo P.C., Lau S.K., Kwok Y.Y., Huang Z. Antibody response of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) to nucleocapsid antigen of SARS-associated coronavirus. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003;23:637–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

