Nuclear factor {kappa}B inactivation in the rat liver ameliorates short term total warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 15888794
- PMCID: PMC1774544
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.043034
Nuclear factor {kappa}B inactivation in the rat liver ameliorates short term total warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
Background: In hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury, activated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells) are dominantly regulated by a transcription factor, nuclear factor kappaB (NFkappaB), with respect to expression of inflammatory cytokines, acute phase response proteins, and cell adhesion molecules.
Aims: We assessed whether inactivation of NFkappaB in the liver could attenuate total hepatic warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury.
Methods: We studied rats with hepatic overexpression of inhibitor kappaBalpha super-repressor (IkappaBalpha SR) caused by a transgene introduced using an adenoviral vector. Hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury was induced under warm conditions by total occlusion of hepatoduodenal ligament structures for 20 minutes, followed by reperfusion. Controls included uninfected and control virus (AdLacZ) infected rats.
Results: IkappaBalpha SR was overexpressed in Kupffer cells as well as in hepatocytes, blocking nuclear translocation of NFkappaB (p65) into the nucleus after reperfusion. Gene transfection with IkappaBalpha SR, but not with LacZ, markedly attenuated ischaemia/reperfusion injury, suppressing inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine expression in the liver. Moreover, no remarkable hepatocyte apoptosis was detected under IkappaBalpha SR overexpression.
Conclusions: Adenoviral transfer of the IkappaBalpha SR gene in the liver ameliorates short term warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury, possibly through attenuation of hepatic macrophage activation.
Figures
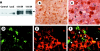
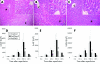


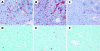
References
-
- Sugawara Y, Kubota K, Ogura T, et al. Increased nitric oxide production in the liver in the perioperative period of partial hepatectomy with Pringle’s maneuver. J Hepatol 1998;28:212–20. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell-Kenkel JC, Currin RT, Tanaka Y, et al. Reperfusion injury to endothelial cells following cold ischemic storage of rat livers. Hepatology 1989;10:292–9. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Farhood A. Neutrophil and Kupffer cell-induced oxidant stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. Am J Physiol 1991;260:G355–62. - PubMed
-
- Lentsch AB, Kato A, Yoshidome H, et al. Inflammatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology 2000;32:169–73. - PubMed
-
- Liu P, McGuire GM, Fisher MA, et al. Activation of Kupffer cells and neutrophils for reactive oxygen formation is responsible for endotoxin-enhanced liver injury after hepatic ischemia. Shock 1995;3:56–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
