Prime role for an insulin epitope in the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice
- PMID: 15889095
- PMCID: PMC1364531
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03523
Prime role for an insulin epitope in the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice
Abstract
A fundamental question about the pathogenesis of spontaneous autoimmune diabetes is whether there are primary autoantigens. For type 1 diabetes it is clear that multiple islet molecules are the target of autoimmunity in man and animal models. It is not clear whether any of the target molecules are essential for the destruction of islet beta cells. Here we show that the proinsulin/insulin molecules have a sequence that is a primary target of the autoimmunity that causes diabetes of the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse. We created insulin 1 and insulin 2 gene knockouts combined with a mutated proinsulin transgene (in which residue 16 on the B chain was changed to alanine) in NOD mice. This mutation abrogated the T-cell stimulation of a series of the major insulin autoreactive NOD T-cell clones. Female mice with only the altered insulin did not develop insulin autoantibodies, insulitis or autoimmune diabetes, in contrast with mice containing at least one copy of the native insulin gene. We suggest that proinsulin is a primary autoantigen of the NOD mouse, and speculate that organ-restricted autoimmune disorders with marked major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction of disease are likely to have specific primary autoantigens.
Figures
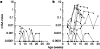
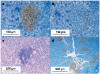
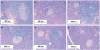
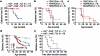
Comment in
-
Immunology: insulin trigger for diabetes.Nature. 2005 May 12;435(7039):151-2. doi: 10.1038/435151a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15889071 No abstract available.
-
Immunology: Insulin auto-antigenicity in type 1 diabetes.Nature. 2005 Nov 24;438(7067):E5; discussion E5-6. doi: 10.1038/nature04423. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16306940
References
-
- Wegmann DR, Norbury-Glaser M, Daniel D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994;24:1853–1857. - PubMed
-
- Abiru N, et al. Dual overlapping peptides recognized by insulin peptide B:9–23 T cell receptor AV13S3 T cell clones of the NOD mouse. J. Autoimmun. 2000;14:231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
