Intronic CA-repeat and CA-rich elements: a new class of regulators of mammalian alternative splicing
- PMID: 15889141
- PMCID: PMC1142610
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600677
Intronic CA-repeat and CA-rich elements: a new class of regulators of mammalian alternative splicing
Abstract
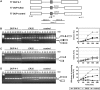
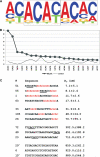
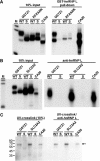
We have recently identified an intronic polymorphic CA-repeat region in the human endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene as an important determinant of the splicing efficiency, requiring specific binding of hnRNP L. Here, we analyzed the position requirements of this CA-repeat element, which revealed its potential role in alternative splicing. In addition, we defined the RNA binding specificity of hnRNP L by SELEX: not only regular CA repeats are recognized with high affinity but also certain CA-rich clusters. Therefore, we have systematically searched the human genome databases for CA-repeat and CA-rich elements associated with alternative 5' splice sites (5'ss), followed by minigene transfection assays. Surprisingly, in several specific human genes that we tested, intronic CA RNA elements could function either as splicing enhancers or silencers, depending on their proximity to the alternative 5'ss. HnRNP L was detected specifically bound to these diverse CA elements. These data demonstrated that intronic CA sequences constitute novel and widespread regulatory elements of alternative splicing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HnRNP L stimulates splicing of the eNOS gene by binding to variable-length CA repeats.Nat Struct Biol. 2003 Jan;10(1):33-7. doi: 10.1038/nsb875. Nat Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12447348
-
Getting to the heart of a splicing enhancer.Nat Struct Biol. 2003 Jan;10(1):6-7. doi: 10.1038/nsb0103-6. Nat Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12490885
-
HnRNP L-mediated regulation of mammalian alternative splicing by interference with splice site recognition.RNA Biol. 2010 Jan-Feb;7(1):56-64. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.1.10402. Epub 2010 Jan 21. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 19946215
-
Exonization of transposed elements: A challenge and opportunity for evolution.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1928-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.014. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21787833 Review.
-
Splice and Dice: Intronic microRNAs, Splicing and Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 19;9(9):1268. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091268. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structures and RNA-binding properties of the RNA recognition motifs of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L: insights into its roles in alternative splicing regulation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 2;288(31):22636-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463901. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23782695 Free PMC article.
-
PLP/DM20 ratio is regulated by hnRNPH and F and a novel G-rich enhancer in oligodendrocytes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):4164-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm387. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567613 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian RNA switches: Molecular rheostats in gene regulation, disease, and medicine.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Oct 24;17:1326-1338. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.10.001. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31741723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Alternative RNA Splicing in Gastrointestinal Malignancies and Other Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 30;22(21):11790. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111790. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multilevel Differential Control of Hormone Gene Expression Programs by hnRNP L and LL in Pituitary Cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 May 29;38(12):e00651-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00651-17. Print 2018 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29610151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilbao D, Valcarcel J (2003) Getting to the heart of a splicing enhancer. Nat Struct Biol 10: 6–7 - PubMed
-
- Black DL (2003) Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem 72: 291–336 - PubMed
-
- Blencowe BJ (2000) Exonic splicing enhancers: mechanism of action, diversity and role in human genetic diseases. Trends Biochem Sci 25: 106–110 - PubMed
-
- Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR (2002) Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet 3: 285–298 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

