H662 is the linchpin of ATP hydrolysis in the nucleotide-binding domain of the ABC transporter HlyB
- PMID: 15889153
- PMCID: PMC1142601
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600657
H662 is the linchpin of ATP hydrolysis in the nucleotide-binding domain of the ABC transporter HlyB
Abstract
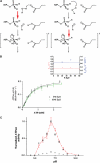
The ABC transporter HlyB is a central element of the HlyA secretion machinery, a paradigm of Type I secretion. Here, we describe the crystal structure of the HlyB-NBD (nucleotide-binding domain) with H662 replaced by Ala in complex with ATP/Mg2+. The dimer shows a composite architecture, in which two intact ATP molecules are bound at the interface of the Walker A motif and the C-loop, provided by the two monomers. ATPase measurements confirm that H662 is essential for activity. Based on these data, we propose a model in which E631 and H662, highly conserved among ABC transporters, form a catalytic dyad. Here, H662 acts as a 'linchpin', holding together all required parts of a complicated network of interactions between ATP, water molecules, Mg2+, and amino acids both in cis and trans, necessary for intermonomer communication. Based on biochemical experiments, we discuss the hypothesis that substrate-assisted catalysis, rather than general base catalysis might operate in ABC-ATPases.
Figures


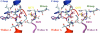

References
-
- Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994) Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria [see comments]. Nature 370: 621–628 - PubMed
-
- Bertchold H, Reshetnikova L, Reiser COA, Schirmer NK, Sprinzl M, Hilgenfeld R (1993) Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature 365: 126–132 - PubMed
-
- Carter P, Abrahmsen L, Wells JA (1991) Probing the mechanism and improving the rate of substrate-assisted catalysis in subtilisin BPN′. Biochemistry 30: 6142–6148 - PubMed
-
- Chang G (2003) Structure of MsbA from Vibrio cholera: a multidrug resistance ABC transporter homolog in a closed conformation. J Mol Biol 330: 419–430 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

