Dengue fever, Hawaii, 2001-2002
- PMID: 15890132
- PMCID: PMC3320380
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1105.041063
Dengue fever, Hawaii, 2001-2002
Abstract
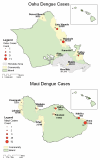
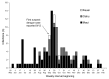
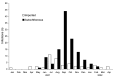
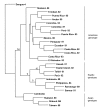
Autochthonous dengue infections were last reported in Hawaii in 1944. In September 2001, the Hawaii Department of Health was notified of an unusual febrile illness in a resident with no travel history; dengue fever was confirmed. During the investigation, 1,644 persons with locally acquired denguelike illness were evaluated, and 122 (7%) laboratory-positive dengue infections were identified; dengue virus serotype 1 was isolated from 15 patients. No cases of dengue hemorrhagic fever or shock syndrome were reported. In 3 instances autochthonous infections were linked to a person who reported denguelike illness after travel to French Polynesia. Phylogenetic analyses showed the Hawaiian isolates were closely associated with contemporaneous isolates from Tahiti. Aedes albopictus was present in all communities surveyed on Oahu, Maui, Molokai, and Kauai; no Ae. aegypti were found. This outbreak underscores the importance of maintaining surveillance and control of potential disease vectors even in the absence of an imminent disease threat.
Figures
References
-
- Gubler DJ. Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever: its history and resurgence as a global public health problem. In: Gubler DJ, Kuno G, editors. Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever. New York: CAB International; 1997. p. 1–22.
-
- Wilson GW. Epidemic of dengue in the territory of Hawaii during 1903. Public Health Rep. 1904;19:67–70.
-
- Usinger RI. Entomological phases of the recent dengue epidemic in Honolulu. Public Health Rep. 1944;59:423–30. 10.2307/4584829 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
