Proteinase-activated receptor-1 mediates elastase-induced apoptosis of human lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 15891109
- PMCID: PMC2715314
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0109OC
Proteinase-activated receptor-1 mediates elastase-induced apoptosis of human lung epithelial cells
Abstract
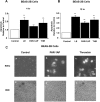
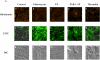
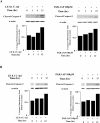
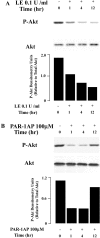
Apoptosis of distal lung epithelial cells plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. In this context, proteinases, either circulating or leukocyte-derived, may contribute to epithelial apoptosis and lung injury. We hypothesized that apoptosis of lung epithelial cells induced by leukocyte elastase is mediated via the proteinase activated receptor (PAR)-1. Leukocyte elastase, thrombin, and PAR-1-activating peptide, but not the control peptide, induced apoptosis in human airway and alveolar epithelial cells as assessed by increases in cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments and TUNEL staining. These effects were largely prevented by a specific PAR-1 antagonist and by short interfering RNA directed against PAR-1. To ascertain the mechanism of epithelial apoptosis, we determined that PAR-1AP, thrombin, and leukocyte elastase dissipated mitochondrial membrane potential, induced translocation of cytochrome c to the cytosol, enhanced cleavage of caspase-9 and caspase-3, and led to JNK activation and Akt inhibition. In concert, these observations provide strong evidence that leukocyte elastase mediates apoptosis of human lung epithelial cells through PAR-1-dependent modulation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway via alterations in mitochondrial permeability and by modulation of JNK and Akt.
Figures











Comment in
-
No bit PARt for PAR-1.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005 Sep;33(3):213-5. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.F304. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16107573 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Leukocyte elastase induces lung epithelial apoptosis via a PAR-1-, NF-kappaB-, and p53-dependent pathway.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Dec;41(6):742-55. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0157OC. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19307610 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte elastase induces epithelial apoptosis: role of mitochondial permeability changes and Akt.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Jul;287(1):G286-98. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00350.2003. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15194561
-
RRR-alpha-tocopheryl succinate-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells involves Bax translocation to mitochondria.Cancer Res. 2003 May 15;63(10):2483-91. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12750270
-
Proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) and cell apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2004 Nov;9(6):729-37. doi: 10.1023/B:APPT.0000045784.49886.96. Apoptosis. 2004. PMID: 15505415 Review.
-
Apoptosis and lung injury.Keio J Med. 2005 Dec;54(4):184-9. doi: 10.2302/kjm.54.184. Keio J Med. 2005. PMID: 16452828 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of protease-activated receptor-2 on cell death and DNA fragmentation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells.J Transl Med. 2010 Sep 16;8:85. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-85. J Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20846373 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic triad in COPD: oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and inflammation.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011;6:413-21. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S10770. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011. PMID: 21857781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absence of proteinase-activated receptor-1 signaling in mice confers protection from fMLP-induced goblet cell metaplasia.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Dec;41(6):680-7. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0386OC. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19307611 Free PMC article.
-
Potent elastase inhibitors from cyanobacteria: structural basis and mechanisms mediating cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in bronchial epithelial cells.J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 14;56(3):1276-90. doi: 10.1021/jm3017305. Epub 2013 Jan 28. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23350733 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of proteolysis in regulation of GPCR function.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;168(3):576-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02234.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23043558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Havemann K, Gramse M. Physiology and pathophysiology of neutral proteinases of human granulocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol 1984;167:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Lee WL, Downey GP. Leukocyte elastase: physiological functions and role in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164:896–904. - PubMed
-
- Cochrane CG, Spragg RG, Revak SD, Cohen AB, McGuire WW. The presence of neutrophil elastase and evidence of oxidation activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 1983;127:S25–S27. - PubMed
-
- Collins JF, Anzueto AA, Peters JI, de los Santos R, Gonzalez DC, Johanson WG Jr, Seidenfeld JJ, Coalson JJ, Jenkinson SG. Elastase activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from oxygen-exposed, Pseudomonas-infected baboons. Lung 1991;169:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Suter PM, Suter S, Girardin E, Roux-Lombard P, Grau GE, Dayer JM. High bronchoalveolar levels of tumor necrosis factor and its inhibitors, interleukin-1, interferon, and elastase, in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome after trauma, shock, or sepsis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992;145:1016–1022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

