Rapid and fully automated visualization of subdural electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy patients
- PMID: 15891163
- PMCID: PMC8158601
Rapid and fully automated visualization of subdural electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy patients
Abstract
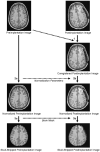
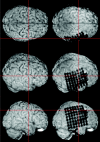
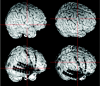
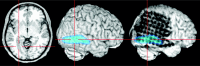
For rapid visualization of subdural electrodes with respect to cortical and subcortical structures, we describe a novel and fully automated method based on coregistration, normalization, optional cerebellum masking, and volume rendering of 3D MR imaging data taken before and after implantation. The key step employs the skull-stripped preimplantation image as a mask to also remove the skull in the postimplantation image. The extracted brain is presented in 3D with the electrodes directly visible by their susceptibility artifacts. Compared with alternative methods, ours is based on freely available software and does not require manual intervention.
Figures
References
-
- Behrens E, Zentner J, van Roost D, et al. Subdural and depth electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1994;128:84–87 - PubMed
-
- Winkler PA, Vollmar C, Krishnan KG, et al. Usefulness of 3-D reconstructed images of the human cerebral cortex for localization of subdural electrodes in epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res 2000;41:169–178 - PubMed
-
- Noordmans HJ, van Rijen PC, van Veelen CW, et al. Localization of implanted EEG electrodes in a virtual-reality environment. Comput Aided Surg 2001;6:241–258 - PubMed
-
- Wellmer J, von Oertzen J, Schaller C, et al. Digital photography and 3D MRI-based multimodal imaging for individualized planning of resective neocortical epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 2002;43:1543–1550 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
