Radiation-induced cavernomas of the brain
- PMID: 15891176
- PMCID: PMC8158583
Radiation-induced cavernomas of the brain
Abstract
The purpose of this report is to add support to the growing literature that there is a correlation between radiation and cavernomas of the brain, particularly if the radiation is received in childhood, as well as to increase awareness of this correlation in the radiology community. Retrospective review of our experience returned five patients who received radiation therapy while they were children and developed cavernomas in the irradiated tissues 3-41 years later. Cavernomas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a hemorrhagic lesion in any patient who has received previous CNS radiation, particularly if he or she underwent radiation therapy in childhood.
Figures

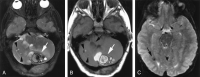
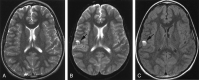
References
-
- Russel DS, Rubinstein LJ. Pathology of Tumors of the Nervous System. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins;1989. :730–736
-
- Rigamonti D, Hadley MN, Drayer BP, et al. Cerebral cavernous malformations: incidence and familial occurrence. N Engl J Med 1988;319:343–347 - PubMed
-
- Ciricillo SF, Cogen PH, Edwards MS. Pediatric cryptic vascular malformations: presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Neurosurg 1994;20:137–147 - PubMed
-
- Heckl S, Aschoff A, Kunze S. Radiation-induced cavernous hemangiomas of the brain: a late effect predominantly in children. Cancer 2002;94:3285–3291 - PubMed
-
- Larson JJ, Ball WS, Bove KE, et al. Formation of intracerebral cavernous malformations after radiation treatment for central nervous system neoplasia in children. J Neurosurg 1998;88:51–56 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
