Allopurinol reduces B-type natriuretic peptide concentrations and haemoglobin but does not alter exercise capacity in chronic heart failure
- PMID: 15894768
- PMCID: PMC1768933
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2004.040477
Allopurinol reduces B-type natriuretic peptide concentrations and haemoglobin but does not alter exercise capacity in chronic heart failure
Abstract
Objective: To study whether the effect of allopurinol on improvement of endothelial dysfunction in chronic heart failure (CHF) translates into improved exercise capacity and to examine whether allopurinol also improves B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), the other important prognostic marker of CHF.
Design: Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover trial.
Setting: Teaching hospital.
Patients: 50 patients with CHF (New York Heart Association functional classes II and III) were recruited.
Interventions: 50 patients with CHF were randomly assigned to three months' treatment with allopurinol (300 mg/day) or placebo. At two and three months into treatment, they underwent a modified Bruce exercise protocol and a six minute walk test. Blood was taken for BNP and haemoglobin analysis.
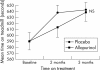
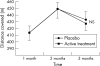
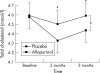
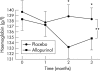
Results: Neither exercise test was altered by allopurinol. However, plasma BNP concentrations fell significantly (p = 0.035) with allopurinol (11.9 pmol/l) versus placebo (14.4 pmol/l). Haemoglobin concentrations also fell highly significantly with allopurinol (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: An important negative finding is that despite high hopes for it, allopurinol had no effect on exercise capacity in CHF. On the other hand, allopurinol did reduce BNP, which is the best available surrogate marker for prognosis in CHF.
Figures

Comment in
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibition for chronic heart failure: is allopurinol the next therapeutic advance in heart failure?Heart. 2005 Jun;91(6):707-9. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2004.057190. Heart. 2005. PMID: 15894755 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Erythropoietin improves anemia exercise tolerance and renal function and reduces B-type natriuretic peptide and hospitalization in patients with heart failure and anemia.Am Heart J. 2006 Dec;152(6):1096.e9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2006.08.005. Am Heart J. 2006. PMID: 17161060 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of spironolactone on endothelial function, vascular angiotensin converting enzyme activity, and other prognostic markers in patients with mild heart failure already taking optimal treatment.Heart. 2004 Jul;90(7):765-70. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.017368. Heart. 2004. PMID: 15201246 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with chronic heart failure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Feb 7;59(6):585-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.10.880. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22300693 Clinical Trial.
-
[Brain natriuretic Peptide. Diagnostic and prognostic value in chronic heart failure].Med Klin (Munich). 2003 Oct 15;98(10):562-7. doi: 10.1007/s00063-003-1304-7. Med Klin (Munich). 2003. PMID: 14586510 Review. German.
-
[Brain natriuretic peptide].Rinsho Byori. 2004 Aug;52(8):655-68. Rinsho Byori. 2004. PMID: 15478621 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Is Hyperuricemia, an Early-Onset Metabolic Disorder, Causally Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Events in Han Chinese?J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 12;8(8):1202. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081202. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31408958 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapy: Xanthine oxidase inhibition for relief of angina pectoris.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Nov;7(11):603-4. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.143. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20975655 No abstract available.
-
Allopurinol and mortality in hyperuricaemic patients.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009 Jul;48(7):804-6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep069. Epub 2009 May 15. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009. PMID: 19447769 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implications of Uric Acid in Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2021 Jan 14;11(1):53. doi: 10.3390/life11010053. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33466609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibition with febuxostat attenuates systolic overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice.J Card Fail. 2008 Nov;14(9):746-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2008.06.006. Epub 2008 Jul 10. J Card Fail. 2008. PMID: 18995179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardillo C, Kilcoyne CM, Cannon RO, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibition with oxypurinol improves endothelial vasodilator function in hypercholesterolaemia but not hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1997;30:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Butler R, Morris AD, Belch JJF, et al. Allopurinol normalises endothelial function in type 2 diabetics with mild hypertension. Hypertension 2000;5:746–51. - PubMed
-
- Guthikonda S, Sinkey C, Barenz T, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibition reverses endothelial dysfunction in heavy smokers. Circulation 2003;107:416–21. - PubMed
-
- Doehner W, Schoene N, Rauchhaus M, et al. Effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition with allopurinol on endothelial function and peripheral blood flow in hyperuricemic patients with chronic heart failure: results from 2 placebo controlled studies. Circulation 2002;105:2619–24. - PubMed
-
- Farquharson C, Butler R, Hill A, et al. Allopurinol improves endothelial dysfunction in chronic heart failure. Circulation 2002;106:221–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
