Explaining the oligomerization properties of the spindle assembly checkpoint protein Mad2
- PMID: 15897186
- PMCID: PMC1569476
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1618
Explaining the oligomerization properties of the spindle assembly checkpoint protein Mad2
Abstract
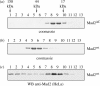
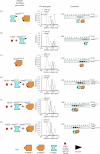
Mad2 is an essential component of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), a molecular device designed to coordinate anaphase onset with the completion of chromosome attachment to the spindle. Capture of chromosome by microtubules occur on protein scaffolds known as kinetochores. The SAC proteins are recruited to kinetochores in prometaphase where they generate a signal that halts anaphase until all sister chromatid pairs are bipolarly oriented. Mad2 is a subunit of the mitotic checkpoint complex, which is regarded as the effector of the spindle checkpoint. Its function is the sequestration of Cdc20, a protein required for progression into anaphase. The function of Mad2 in the checkpoint correlates with a dramatic conformational rearrangement of the Mad2 protein. Mad2 adopts a closed conformation (C-Mad2) when bound to Cdc20, and an open conformation (O-Mad2) when unbound to this ligand. Checkpoint activation promotes the conversion of O-Mad2 to Cdc20-bound C-Mad2. We show that this conversion requires a C-Mad2 template and we identify this in Mad1-bound Mad2. In our proposition, Mad1-bound C-Mad2 recruits O-Mad2 to kinetochores, stimulating Cdc20 capture, implying that O-Mad2 and C-Mad2 form dimers. We discuss Mad2 oligomerization and link our discoveries to previous observations related to Mad2 oligomerization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Mad1/Mad2 complex as a template for Mad2 activation in the spindle assembly checkpoint.Curr Biol. 2005 Feb 8;15(3):214-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.038. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15694304
-
Accumulation of Mad2-Cdc20 complex during spindle checkpoint activation requires binding of open and closed conformers of Mad2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul 3;174(1):39-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200602109. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16818718 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic analysis of Mad2-Cdc20 formation: conformational changes in Mad2 are catalyzed by a C-Mad2-ligand complex.Biochemistry. 2009 Oct 13;48(40):9503-15. doi: 10.1021/bi900718e. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19719327
-
Checkpoint signalling: Mad2 conformers and signal propagation.Curr Biol. 2005 Feb 22;15(4):R122-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.008. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15723780 Review.
-
Structural activation of Mad2 in the mitotic spindle checkpoint: the two-state Mad2 model versus the Mad2 template model.J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr 24;173(2):153-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601172. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16636141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of conformational dimerization of Mad2 and its inhibition by p31comet.EMBO J. 2006 Mar 22;25(6):1273-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601033. Epub 2006 Mar 9. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16525508 Free PMC article.
-
Basic mechanism of eukaryotic chromosome segregation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Mar 29;360(1455):609-21. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1615. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15897183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage induced p53 downregulates Cdc20 by direct binding to its promoter causing chromatin remodeling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 May;37(8):2688-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp110. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19273532 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational dynamics of the Hop1 HORMA domain reveal a common mechanism with the spindle checkpoint protein Mad2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 9;46(1):279-292. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1196. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29186573 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling dual pathways for the metazoan spindle assembly checkpoint.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 7;103(45):16758-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603174103. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17065324 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

