REM restriction persistently alters strategy used to solve a spatial task
- PMID: 15897251
- PMCID: PMC1142465
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.84805
REM restriction persistently alters strategy used to solve a spatial task
Abstract
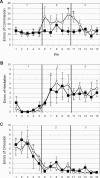
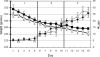
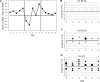
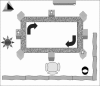
We tested the hypothesis that rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is important for complex associative learning by restricting rats from entering REM sleep for 4 h either immediately after training on an eight-box spatial task (0-4 REMr) or 4 h following training (4-8 REMr). Both groups of REM-restricted rats eventually reached the same overall performance level as did nonrestricted controls, but 0-4 REMr animals were delayed in their improvement in the first few days and lagged behind controls in the middle portion of the training period. More importantly, performance gains of 0-4 REMr rats depended more on simple local cues throughout the 15-d study since, unlike control and 4-8 REMr animals, their error rate increased after daily disruption of the relationship between local (intramaze) cues and the food reward. Thus, although overall performance was only subtly and transiently impaired, due to the ability to use alternate, nonspatial behavioral strategies, complex associative (spatial) learning was persistently impaired by restricting REM for a short critical period each day.
Figures


References
-
- Barnes, C.A., Nadel, L., and Honig, W.K. 1980. Spatial memory deficit in senescent rats. Can. J. Psychol. 34: 29-39. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, C.A., Suster, M.S., Shen, J., and McNaughton, B.L. 1997. Multistability of cognitive maps in the hippocampus of old rats. Nature 388: 272-275. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet, M.H. and Arand, D.L. 1994. The use of prophylactic naps and caffeine to maintain performance during a continuous operation. Ergonomics 37: 1009-1020. - PubMed
-
- Borbely, A.A. 1980. Effects of light and circadian rhythm on the occurrence of REM sleep in the rat. Sleep 2: 289-298. - PubMed
-
- Borbely, A.A. and Neuhaus, H.U. 1979. Sleep-deprivation: Effects on sleep and EEG in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. 133: 71-87.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
