Shared reactivity of V{delta}2(neg) {gamma}{delta} T cells against cytomegalovirus-infected cells and tumor intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 15897274
- PMCID: PMC2212929
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041851
Shared reactivity of V{delta}2(neg) {gamma}{delta} T cells against cytomegalovirus-infected cells and tumor intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
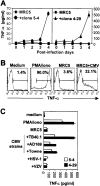
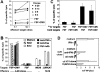
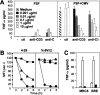
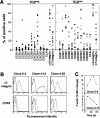
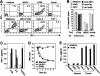
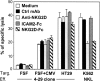
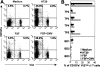
Long-lasting expansion of Vdelta2(neg) gammadelta T cells is a hallmark of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in kidney transplant recipients. The ligands of these cells and their role remain elusive. To better understand their immune function, we generated gammadelta T cell clones from several transplanted patients. Numerous patient Vdelta1(+), Vdelta3(+), and Vdelta5(+) gammadelta T cell clones expressing diverse Vgamma chains, but not control Vgamma9Vdelta2(+) T clones, displayed strong reactivity against CMV-infected cells, as shown by their production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Vdelta2(neg) gammadelta T lymphocytes could also kill CMV-infected targets and limit CMV propagation in vitro. Their anti-CMV reactivity was specific for this virus among herpesviridae and required T cell receptor engagement, but did not involve major histocompatibility complex class I molecules or NKG2D. Vdelta2(neg) gammadelta T lymphocytes expressed receptors essential for intestinal homing and were strongly activated by intestinal tumor, but not normal, epithelial cell lines. High frequencies of CMV- and tumor-specific Vdelta2(neg) gammadelta T lymphocytes were found among patients' gammadelta T cells. In conclusion, Vdelta2(neg) gammadelta T cells may play a role in protecting against CMV and tumors, probably through mucosal surveillance of cellular stress, and represent a population that is largely functionally distinct from Vgamma9Vdelta2(+) T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct and Indirect Effects of Cytomegalovirus-Induced γδ T Cells after Kidney Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 21;6:3. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00003. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25653652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor activity of gammadelta T cells reactive against cytomegalovirus-infected cells in a mouse xenograft tumor model.Cancer Res. 2009 May 1;69(9):3971-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3037. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19383918
-
Cytomegalovirus drives Vδ2neg γδ T cell inflation in many healthy virus carriers with increasing age.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Jun;176(3):418-28. doi: 10.1111/cei.12297. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24547915 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of effector memory Vδ2neg γδ T cells associates with cytomegalovirus reactivation in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 10;15:1397483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397483. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38915409 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of gammadelta T cells in tumor immunology.Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 1;67(1):5-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3069. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17210676 Review.
Cited by
-
Extensive expansion of primary human gamma delta T cells generates cytotoxic effector memory cells that can be labeled with Feraheme for cellular MRI.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Mar;62(3):571-83. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1353-y. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23100099 Free PMC article.
-
TCR-dependent sensitization of human γδ T cells to non-myeloid IL-18 in cytomegalovirus and tumor stress surveillance.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Feb 3;4(5):e1003011. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2014.1003011. eCollection 2015 May. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26155394 Free PMC article.
-
The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).Viruses. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):1455. doi: 10.3390/v12121455. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33348583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraepithelial Lymphocytes of the Intestine.Annu Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;42(1):289-316. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-090222-100246. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Annu Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38277691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct and Indirect Effects of Cytomegalovirus-Induced γδ T Cells after Kidney Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 21;6:3. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00003. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25653652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Constant, P., F. Davodeau, M.A. Peyrat, Y. Poquet, G. Puzo, M. Bonneville, and J.J. Fournié. 1994. Stimulation of human γδ T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 264:267–270. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka, Y., C.T. Morita, E. Nieves, M.B. Brenner, and B.R. Bloom. 1995. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human γδ T cells. Nature. 375:155–158. - PubMed
-
- Kunzmann, V., E. Bauer, J. Feurle, F. Weissinger, H.P. Tony, and M. Wilhelm. 2000. Stimulation of gammadelta T cells by aminobisphosphonates and induction of antiplasma cell activity in multiple myeloma. Blood. 96:384–392. - PubMed
-
- Bukowski, J.F., C.T. Morita, and M.B. Brenner. 1999. Human gamma delta T cells recognize alkylamines derived from microbes, edible plants, and tea: implications for innate immunity. Immunity. 11:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Scotet, E., L.O. Martinez, E. Grant, R. Barbaras, P. Jeno, M. Guiraud, B. Monsarrat, X. Saulquin, S. Maillet, J.P. Esteve, et al. 2005. Tumor recognition following Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell receptor interactions with a surface F1-ATPase-related structure and apolipoprotein A-I. Immunity. 22:71–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

