The amino terminus of Slob, Slowpoke channel binding protein, critically influences its modulation of the channel
- PMID: 15897294
- PMCID: PMC2234080
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200509252
The amino terminus of Slob, Slowpoke channel binding protein, critically influences its modulation of the channel
Abstract
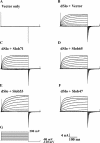
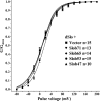
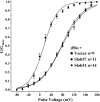
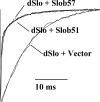
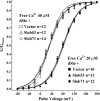
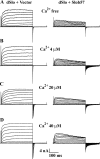
The Drosophila Slowpoke calcium-dependent potassium channel (dSlo) binding protein Slob was discovered by a yeast two-hybrid screen using the carboxy-terminal tail region of dSlo as bait. Slob binds to and modulates the dSlo channel. We have found that there are several Slob proteins, resulting from multiple translational start sites and alternative splicing, and have named them based on their molecular weights (in kD). The larger variants, which are initiated at the first translational start site and are called Slob71 and Slob65, shift the voltage dependence of dSlo activation, measured by the whole cell conductance-voltage relationship, to the left (less depolarized voltages). Slob53 and Slob47, initiated at the third translational start site, also shift the dSlo voltage dependence to the left. In contrast, Slob57 and Slob51, initiated at the second translational start site, shift the conductance-voltage relationship of dSlo substantially to more depolarized voltages, cause an apparent dSlo channel inactivation, and increase the deactivation rate of the channel. These results indicate that the amino-terminal region of Slob plays a critical role in its modulation of dSlo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of two modulatory actions of the channel-binding protein Slob on the Drosophila Slowpoke calcium-dependent potassium channel.J Gen Physiol. 2006 Nov;128(5):583-91. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200609653. J Gen Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17074977 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of variants of slob, slowpoke channel binding protein, in Drosophila.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Mar;95(3):1957-65. doi: 10.1152/jn.00427.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 7. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16339006
-
An interaction domain in Slob necessary for its binding to the slowpoke calcium-dependent potassium channel.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Nov;45(6):714-9. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00285-5. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 14529710
-
High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006 Dec;7(12):921-31. doi: 10.1038/nrn1992. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17115074 Review.
-
Voltage-dependent calcium channels.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2005 Jun;24 Suppl 1:1-78. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2005. PMID: 16096350 Review.
Cited by
-
Slob, a Slowpoke channel-binding protein, modulates synaptic transmission.J Gen Physiol. 2011 Feb;137(2):225-38. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201010439. J Gen Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21282401 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in transmitter release triggers homeostatic transcriptional changes that increase presynaptic excitability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 5;122(31):e2322714122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322714122. Epub 2025 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40729383 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo role of a potassium channel-binding protein in regulating neuronal excitability and behavior.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 21;29(42):13328-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3024-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19846720 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Maxi Calcium-Activated Potassium (BK) Channels.Biomolecules. 2015 Aug 17;5(3):1870-911. doi: 10.3390/biom5031870. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26287261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-specific fine-tuning of neuronal excitability by differential expression of modulator protein isoforms.J Neurosci. 2013 Oct 16;33(42):16767-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1001-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24133277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelman, J.P., K.-Z. Shen, M.P. Kavanaugh, R.A. Warren, Y.-N. Wu, A. Lagrutta, C.T. Bond, and R.A. North. 1992. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, N.S., R. Brenner, R.A. Bohm, J.Y. Yu, and J.L. Wilbur. 1998. Behavioral and electrophysiological analysis of Ca-activated K-channel transgenes in Drosophila. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 860:296–305. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, N.S., G.A. Robertson, and B. Ganetzky. 1991. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 253:551–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

