Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib
- PMID: 15897464
- PMCID: PMC1129023
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502860102
Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib
Abstract
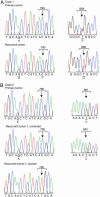
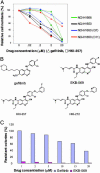
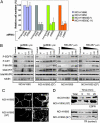
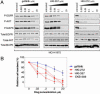
Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) with activating mutations in the kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) demonstrate dramatic, but transient, responses to the reversible tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib (Iressa) and erlotinib (Tarceva). Some recurrent tumors have a common secondary mutation in the EGFR kinase domain, T790M, conferring drug resistance, but in other cases the mechanism underlying acquired resistance is unknown. In studying multiple sites of recurrent NSCLCs, we detected T790M in only a small percentage of tumor cells. To identify additional mechanisms of acquired resistance to gefitinib, we used NSCLC cells harboring an activating EGFR mutation to generate multiple resistant clones in vitro. These drug-resistant cells demonstrate continued dependence on EGFR and ERBB2 signaling for their viability and have not acquired secondary EGFR mutations. However, they display increased internalization of ligand-activated EGFR, consistent with altered receptor trafficking. Although gefitinib-resistant clones are cross-resistant to related anilinoquinazolines, they demonstrate sensitivity to a class of irreversible inhibitors of EGFR. These inhibitors also show effective inhibition of signaling by T790M-mutant EGFR and killing of NSCLC cells with the T790M mutation. Both mechanisms of gefitinib resistance are therefore circumvented by irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Our findings suggest that one of these, HKI-272, may prove highly effective in the treatment of EGFR-mutant NSCLCs, including tumors that have become resistant to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Figures
References
-
- Lynch, T. J., Bell, D. W., Sordella, R., Gurubhagavatula, S., Okimoto, R. A., Brannigan, B. W., Harris, P. L., Haserlat, S. M., Supko, J. G., Haluska, F. G., et al. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez, J. G., Janne, P. A., Lee, J. C., Tracy, S., Greulich, H., Gabriel, S., Herman, P., Kaye, F. J., Lindeman N., Boggon, T. J., et al. (2004) Science 304, 1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Wakeling, A. E., Guy, S. P., Woodburn, J. R., Ashton, S. E., Curry, B. J., Barker, A. J. & Gibson, K. H. (2002) Cancer Res. 62, 5749–5754. - PubMed
-
- Moyer, J. D., Barbacci, E. G., Iwata, K. K., Arnold, L., Boman, B., Cunningham, A., DiOrio, C., Doty, J., Morin, M. J., Moyer, M. P., et al. (1997) Cancer Res. 57, 4838–4848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

