Gene expression profiling of cancer progression reveals intrinsic regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors from transgenic mice
- PMID: 15897883
- PMCID: PMC1431507
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208712
Gene expression profiling of cancer progression reveals intrinsic regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors from transgenic mice
Abstract
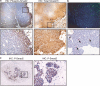
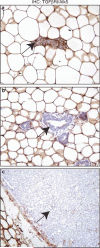
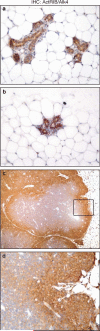
Upregulation of HER2/ErbB2/Neu occurs in 15-30% of human breast cancers and correlates with poor prognosis. Identification of ErbB2/Neu transcriptional targets should facilitate development of novel therapeutic approaches. Development of breast cancer is a multistep process; thus, to identify the transcriptomes associated with different stages of progression of tumorigenesis, we compared expression profiles of mammary tumors and preneoplastic mammary tissue from MMTV-Neu transgenic mice to expression profiles of wild-type mammary glands using Affymetrix microarrays. We identified 324 candidate genes that were unique to ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors relative to normal mammary gland tissue from wild-type controls. Expression of a subset of these genes (82) was also changed in the preneoplastic mammary glands compared to wild-type controls, indicating that they may play a pivotal role during early events of ErbB2/Neu-initiated mammary tumorigenesis. Further analysis of the microarray data revealed that expression of several known transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta target genes was altered, suggesting that the TGF-beta signaling cascade is downregulated in ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors. Western blot analysis for TGF-beta-Receptor-I/ALK5 and immunohistochemistry for TGF-beta-Receptor-I/ALK5 and phosphorylated/activated Smad2 confirmed that the Smad-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade was inactive in these tumors. Although absent in most of the tumor, phosphorylated Smad2 was present in the periphery of tumors. Interestingly, presence of phosphorylated/activated Smad2 correlated with expression of Activin-Receptor-IB/ALK4, suggesting that although Smad-dependent TGF-beta signaling is absent in ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors, Activin signaling may be active at the leading edge of these tumors. Cumulatively, these data indicate that the TGF-beta pathway is intrinsically suppressed in ErbB2/Neu tumors via a mechanism involving loss of TGF-beta-Receptor-I/ALK5.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sustained trophism of the mammary gland is sufficient to accelerate and synchronize development of ErbB2/Neu-induced tumors.Oncogene. 2006 Jun 1;25(23):3325-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209365. Epub 2006 Jan 23. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16434967 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction between mouse erbB3 and wild-type rat c-neu in transgenic mouse mammary tumor cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(5):R708-18. doi: 10.1186/bcr1281. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Breast Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16168116 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Smad signaling in human breast carcinoma are associated with poor outcome: a tissue microarray study.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 15;62(2):497-505. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11809701
-
Co-opted integrin signaling in ErbB2-induced mammary tumor progression.Cancer Cell. 2006 Aug;10(2):93-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.07.015. Cancer Cell. 2006. PMID: 16904607 Review.
-
Regulation of mouse mammary gland development and tumorigenesis by the ERBB signaling network.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2001 Jan;6(1):7-21. doi: 10.1023/a:1009560330359. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2001. PMID: 11467454 Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 inhibits tumorigenic progression and metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer.Neoplasia. 2011 Jul;13(7):601-10. doi: 10.1593/neo.11260. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21750654 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) and cancer-oncogene understudy or understudied oncogene?Tumour Biol. 2014 Aug;35(8):7369-82. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2006-x. Epub 2014 May 6. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24798974 Review.
-
Testes-specific protease 50 promotes cell proliferation via inhibiting activin signaling.Oncogene. 2017 Oct 26;36(43):5948-5957. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.198. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28650473
-
Activin receptor-like kinases: a diverse family playing an important role in cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;6(11):2431-2447. eCollection 2016. Am J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27904762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER2/ErbB2-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion require p120 catenin activation of Rac1 and Cdc42.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 17;285(38):29491-501. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136770. Epub 2010 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20595387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alroy I, Yarden Y. FEBS Lett. 1997;410:83, 86. - PubMed
-
- Andrechek ER, Laing MA, Girgis-Gabardo AA, Siegel PM, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4920–4926. - PubMed
-
- Bertucci F, Borie N, Ginestier C, Groulet A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Adelaide J, Geneix J, Bachelart L, Finetti P, Koki A, Hermitte F, Hassoun J, Debono S, Viens P, Fert V, Jacquemier J, Birnbaum D. Oncogene. 2004;23:2564–2575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

