Antigenic cross-reactivity between severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus and human coronaviruses 229E and OC43
- PMID: 15897988
- PMCID: PMC7109809
- DOI: 10.1086/430355
Antigenic cross-reactivity between severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus and human coronaviruses 229E and OC43
Abstract
Cross-reactivity between antibodies to different human coronaviruses (HCoVs) has not been systematically studied. By use of Western blot analysis, indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), antigenic cross-reactivity between severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and 2 HCoVs (229E and OC43) was demonstrated in immunized animals and human serum. In 5 of 11 and 10 of 11 patients with SARS, paired serum samples showed a > or =4-fold increase in antibody titers against HCoV-229E and HCoV-OC43, respectively, by IFA. Overall, serum samples from convalescent patients who had SARS had a 1-way cross-reactivity with the 2 known HCoVs. Antigens of SARS-CoV and HCoV-OC43 were more cross-reactive than were those of SARS-CoV and HCoV-229E.
Figures
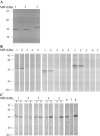
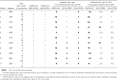
References
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–66. - PubMed
-
- Myint SH. Human coronavirus infections. In: Siddell SG, editor. The Coronaviridae. New York: Plenum Press; 1995. pp. 389–401.
-
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

