Bim regulation of lumen formation in cultured mammary epithelial acini is targeted by oncogenes
- PMID: 15899862
- PMCID: PMC1140636
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.11.4591-4601.2005
Bim regulation of lumen formation in cultured mammary epithelial acini is targeted by oncogenes
Abstract
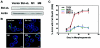
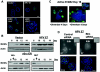
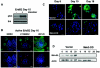
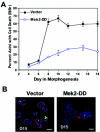
Epithelial cells organize into cyst-like structures that contain a spherical monolayer of cells that enclose a central lumen. Using a three-dimensional basement membrane culture model in which mammary epithelial cells form hollow, acinus-like structures, we previously demonstrated that lumen formation is achieved, in part, through apoptosis of centrally localized cells. We demonstrate that the proapoptotic protein Bim may selectively trigger apoptosis of the centrally localized acinar cells, leading to temporally controlled lumen formation. Bim is not detectable during early stages of three-dimensional mammary acinar morphogenesis and is then highly upregulated in all cells of acini, coincident with detection of apoptosis in the centrally localized acinar cells. Inhibition of Bim expression by RNA interference transiently blocks luminal apoptosis and delays lumen formation. Oncogenes that induce acinar luminal filling, such as ErbB2 and v-Src, suppress expression of Bim through a pathway dependent on Erk-mitogen-activated protein kinase; however, HPV 16 E7, an oncogene that stimulates cell proliferation but not luminal filling, is unable to reduce Bim expression. Thus, Bim is a critical regulator of luminal apoptosis during mammary acinar morphogenesis in vitro and may be an important target of oncogenes that disrupt glandular epithelial architecture.
Figures



References
-
- Biswas, S. C., and L. A. Greene. 2002. NGF down-regulates the BH3-only protein Bim and suppresses its proapoptotic activity by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:49511-49516. - PubMed
-
- Blatchford, D. R., L. H. Quarrie, E. Tonner, C. McCarthy, D. J. Flint, and C. J. Wilde. 1999. Influence of microenvironment on mammary epithelial cell survival in primary culture. J. Cell Physiol. 181:304-311. - PubMed
-
- Bouillet, P., S. Cory, L. C. Zhang, A. Strasser, and J. M. Adams. 2001. Degenerative disorders caused by Bcl-2 deficiency prevented by loss of its BH3-only antagonist Bim. Dev. Cell 1:645-653. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, E. H., M. C. Wei, S. Weiler, R. A. Flavell, T. W. Mak, T. Lindsten, and S. J. Korsmeyer. 2001. BCL-2, BCL-X(L) sequester BH3 domain-only molecules preventing BAX- and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 8:705-711. - PubMed
-
- Coucouvanis, E., and G. R. Martin. 1999. BMP signaling plays a role in visceral endoderm differentiation and cavitation in the early mouse embryo. Development 126:535-546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
