The C. elegans homolog of the mammalian tumor suppressor Dep-1/Scc1 inhibits EGFR signaling to regulate binary cell fate decisions
- PMID: 15901674
- PMCID: PMC1142556
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.333505
The C. elegans homolog of the mammalian tumor suppressor Dep-1/Scc1 inhibits EGFR signaling to regulate binary cell fate decisions
Abstract
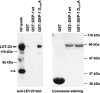
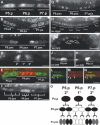
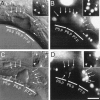
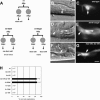
Protein phosphorylation by kinases and the subsequent dephosphorylation by phosphatases are key mechanisms that regulate intracellular signal transduction during development. Here, we report the identification of the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase DEP-1 as a negative regulator of the Caenorhabditis elegans EGF receptor. DEP-1 amplifies in the developing vulva and the excretory system the small differences in the amount of EGF signal received by equivalent precursor cells to achieve binary cell fate decisions. During vulval development, DEP-1 inhibits EGFR signaling in the secondary cell lineage in parallel with the NOTCH-mediated lateral inhibition, while EGFR signaling simultaneously down-regulates DEP-1 and NOTCH expression in the primary cell lineage. This regulatory network of inhibitors results in the full activation of the EGFR/RAS/MAPK pathway in the primary vulval cells and at the same time keeps the EGFR/RAS/MAPK pathway inactive in the adjacent secondary cells. Mammalian Dep-1/Scc1 functions as a tumor-suppressor gene in the intestinal epithelium. Thus, mutations in human Dep-1 may promote tumor formation through a hyperactivation of the EGF receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso A., Sasin, J., Bottini, N., Friedberg, I., Osterman, A., Godzik, A., Hunter, T., Dixon, J., and Mustelin, T. 2004. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117: 699-711. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. 1999. Cell cycle-dependent sequencing of cell fate decisions in Caenorhabditis elegans vulva precursor cells. Development 126: 1947-1956. - PubMed
-
- Berset T., Hoier, E.F., Battu, G., Canevascini, S., and Hajnal, A. 2001. Notch inhibition of RAS signaling through MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 during C. elegans vulval development. Science 291: 1055-1058. - PubMed
-
- Bhaduri A. and Sowdhamini, R. 2003. A genome-wide survey of human tyrosine phosphatases. Protein Eng. 16: 881-888. - PubMed
-
- Blanchetot C., Chagnon, M., Dube, N., Halle, M., and Tremblay, M.L. 2005. Substrate-trapping techniques in the identification of cellular PTP targets. Methods 35: 44-53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
