Regulation of NMDA receptors by neuregulin signaling in prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 15901778
- PMCID: PMC6724849
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1086-05.2005
Regulation of NMDA receptors by neuregulin signaling in prefrontal cortex
Abstract
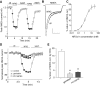
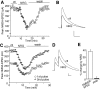
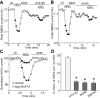
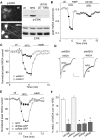
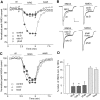
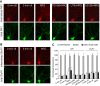
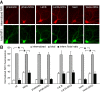
Recent linkage studies have identified a significant association of the neuregulin gene with schizophrenia, but how neuregulin is involved in schizophrenia is primarily unknown. Aberrant NMDA receptor functions have been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Therefore, we hypothesize that neuregulin, which is present in glutamatergic synaptic vesicles, may affect NMDA receptor functions via actions on its ErbB receptors enriched in postsynaptic densities, hence participating in emotional regulation and cognitive processes that are impaired in schizophrenia. To test this, we examined the regulation of NMDA receptor currents by neuregulin signaling pathways in prefrontal cortex (PFC), a prominent area affected in schizophrenia. We found that bath perfusion of neuregulin significantly reduced whole-cell NMDA receptor currents in acutely isolated and cultured PFC pyramidal neurons and decreased NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in PFC slices. The effect of neuregulin was mainly blocked by application of the ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor, IP3 receptor (IP3R) antagonist, or Ca2+ chelators. The neuregulin regulation of NMDA receptor currents was also markedly attenuated in cultured neurons transfected with mutant forms of Ras or a dominant-negative form of MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1). Moreover, the neuregulin effect was prevented by agents that stabilize or disrupt actin polymerization but not by agents that interfere with microtubule assembly. Furthermore, neuregulin treatment increased the abundance of internalized NMDA receptors in cultured PFC neurons, which was also sensitive to agents affecting actin cytoskeleton. Together, our study suggests that both PLC/IP3R/Ca2+ and Ras/MEK/ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) signaling pathways are involved in the neuregulin-induced reduction of NMDA receptor currents, which is likely through enhancing NR1 internalization via an actin-dependent mechanism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of NMDA receptors by dopamine D4 signaling in prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 29;23(30):9852-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09852.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14586014 Free PMC article.
-
D2-class dopamine receptor inhibition of NMDA currents in prefrontal cortical neurons is platelet-derived growth factor receptor-dependent.J Neurochem. 2006 Sep;98(5):1657-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04064.x. Epub 2006 Jul 31. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16879713
-
Dopamine D1 receptors co-distribute with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid type-1 subunits and modulate synaptically-evoked N-methyl-D-aspartic acid currents in rat basolateral amygdala.Neuroscience. 2006 Oct 27;142(3):671-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.059. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16905271
-
Neuregulin 1-erbB4 pathway in schizophrenia: From genes to an interactome.Brain Res Bull. 2010 Sep 30;83(3-4):132-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.04.011. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Brain Res Bull. 2010. PMID: 20433909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ameliorating prefrontal cortical dysfunction in mental illness: inhibition of phosphotidyl inositol-protein kinase C signaling.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Jan;202(1-3):445-55. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1274-9. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 18719894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NMDA hypofunction as a convergence point for progression and symptoms of schizophrenia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 27;7:31. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00031. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23543703 Free PMC article.
-
mGluR1-Dependent Long Term Depression in Rodent Midbrain Dopamine Neurons Is Regulated by Neuregulin 1/ErbB Signaling.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Oct 1;11:346. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00346. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30327588 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB4 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons is critical for neuregulin 1 regulation of long-term potentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 14;107(50):21818-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010669107. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21106764 Free PMC article.
-
Deficient NRG1-ERBB signaling alters social approach: relevance to genetic mouse models of schizophrenia.J Neurodev Disord. 2009 Dec;1(4):302-12. doi: 10.1007/s11689-009-9017-8. Epub 2009 May 27. J Neurodev Disord. 2009. PMID: 21547722 Free PMC article.
-
Dysconnection in schizophrenia: from abnormal synaptic plasticity to failures of self-monitoring.Schizophr Bull. 2009 May;35(3):509-27. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn176. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Schizophr Bull. 2009. PMID: 19155345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anton ES, Marchionni MA, Lee KF, Rakic P (1997) Role of GGF/neuregulin signaling in interactions between migrating neurons and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex. Development 124: 3501-3510. - PubMed
-
- Buonanno A, Fischbach GD (2001) Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11: 287-296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
