Mitochondrial genome sequences support ancient population expansion in Plasmodium vivax
- PMID: 15901839
- PMCID: PMC1224720
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msi168
Mitochondrial genome sequences support ancient population expansion in Plasmodium vivax
Abstract
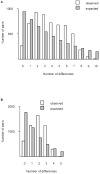
Examination of nucleotide diversity in 106 mitochondrial genomes of the most geographically widespread human malaria parasite, Plasmodium vivax, revealed a level of diversity similar to, but slightly higher than, that seen in the virulent human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The pairwise distribution of nucleotide differences among mitochondrial genome sequences supported the hypothesis that both these parasites underwent ancient population expansions. We estimated the age of the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of the mitochondrial genomes of both P. vivax and P. falciparum at around 200,000-300,000 years ago. This is close to the previous estimates of the time of the human mitochondrial MRCA and the origin of modern Homo sapiens, consistent with the hypothesis that both these Plasmodium species were parasites of the hominid lineage before the origin of modern H. sapiens and that their population expansion coincided with the population expansion of their host.
Figures

References
-
- Anton SC. Natural history of Homo erectus Yearbook Phys. Anthropol. 2003;46:126–170. - PubMed
-
- Conway DJ, Fanello C, Lloyd JM, Al-Joubouri BM-AS, Baloch AH, Somanth SD, Roper C, Oduola AMJ, Mulder B, Povoa MM, Singh B, Thomas AW. Origin of Plasmodium falciparum malaria is traced by mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2000;111:163–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

