FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator
- PMID: 15902306
- PMCID: PMC1088017
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23606
FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator
Abstract
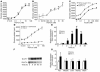
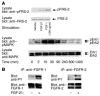
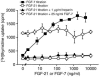
Diabetes mellitus is a major health concern, affecting more than 5% of the population. Here we describe a potential novel therapeutic agent for this disease, FGF-21, which was discovered to be a potent regulator of glucose uptake in mouse 3T3-L1 and primary human adipocytes. FGF-21-transgenic mice were viable and resistant to diet-induced obesity. Therapeutic administration of FGF-21 reduced plasma glucose and triglycerides to near normal levels in both ob/ob and db/db mice. These effects persisted for at least 24 hours following the cessation of FGF-21 administration. Importantly, FGF-21 did not induce mitogenicity, hypoglycemia, or weight gain at any dose tested in diabetic or healthy animals or when overexpressed in transgenic mice. Thus, we conclude that FGF-21, which we have identified as a novel metabolic factor, exhibits the therapeutic characteristics necessary for an effective treatment of diabetes.
Figures
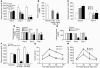
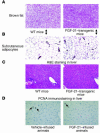
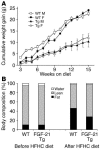
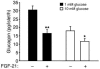
References
-
- McKeehan WL, Wang F, Kan M. The heparan sulfate-fibroblast growth factor family: diversity of structure and function. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1998;59:135–176. - PubMed
-
- Galzie Z, Kinsella AR, Smith JA. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997;75:669–685. - PubMed
-
- Powers CJ, McLeskey SW, Wellstein A. Fibroblast growth factors, their receptors and signaling. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2000;7:165–197. - PubMed
-
- Hogan BL. Morphogenesis. Cell. 1999;96:225–233. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

