Coronary thrombosis related to use of Xenadrine RFA
- PMID: 15902827
- PMCID: PMC555829
Coronary thrombosis related to use of Xenadrine RFA
Abstract
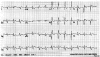
Recently, ephedra was removed from the U.S. marketplace due to a heightened concern that dietary supplements containing ephedra may present "an unreasonable risk of illness or injury." This is the 1st time the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has banned an herbal supplement, and the ban sheds light on the potential harm of nutritional supplements that are used for weight loss or as a boost to athletic performance. We report the case of a body builder who used Xenadrine RFA, an ephedra-containing supplement, at recommended doses for nearly a year; he then experienced an acute myocardial infarction, which was documented to be secondary to thrombosis in situ. We ruled out other possible causes of myocardial infarction, as well a hypercoagulable state. There was no evidence of illicit drug use. Our report serves as a poignant reminder of the potential dangers of herbal supplementation, especially when used to heighten athletic performance.
Figures


References
-
- Haller CA, Benowitz NL. Adverse cardiovascular and central nervous system events associated with dietary supplements containing ephedra alkaloids. N Engl J Med 2000; 343:1833–8. - PubMed
-
- Samenuk D, Link MS, Homoud MK, Contreras R, Theoharides TC, Wang PJ, et al. Adverse cardiovascular events temporally associated with ma huang, an herbal source of ephedrine [published erratum appears in Mayo Clin Proc 2003;78:1055]. Mayo Clin Proc 2002;77:12–6. - PubMed
-
- Cockings JG, Brown M. Ephedrine abuse causing acute myocardial infarction. Med J Aust 1997;167:199–200. - PubMed
-
- Theoharides TC. Sudden death of a healthy college student related to ephedrine toxicity from a ma huang-containing drink. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1997;17:437–9. - PubMed
-
- Zaacks SM, Klein L, Tan CD, Rodriguez ER, Leikin JB. Hypersensitivity myocarditis associated with ephedra use. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 1999;37:485–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
