Fibre-type specificity of interleukin-6 gene transcription during muscle contraction in rat: association with calcineurin activity
- PMID: 15905211
- PMCID: PMC1464774
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089193
Fibre-type specificity of interleukin-6 gene transcription during muscle contraction in rat: association with calcineurin activity
Abstract
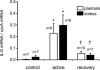
In this study, we quantified the transcription of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene in individual fibres and the associated changes in calcineurin activity assessed at the cellular level during prolonged muscle contraction. Individual myofibres were isolated from plantaris and soleus muscles of rats at the end of an exhaustive running exercise test (n = 10), categorized according to their myosin heavy chain isoform content, and compared to those of resting rats (n = 10). Using real-time PCR analysis in individual fibres, a marked rise in IL-6 transcript levels occurred in type I and IIa fibres at the end of exercise (P < 0.05). Transcription of the gene encoding for the modulatory calcineurin-interacting protein-1 (MCIP-1), a sensitive indicator of calcineurin activity, also mainly increased in type I and IIa fibres (P < 0.05). Moreover, a slight increase in MCIP-1 mRNA levels was observed in type IIx (P < 0.05). Fibre types determined by immunohistochemistry were qualitatively examined for glycogen content using periodic acid-Shiff staining, and no direct relationship was found, at the cellular level, between glycogen content, fibre-type and IL-6 transcription. Our data clearly suggest that IL-6 gene transcription was mainly observed in early recruited myofibres and that contraction-induced IL-6 transcription could be associated with enhanced calcineurin activity.
Figures
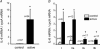

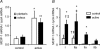
Similar articles
-
Exercise-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in rat skeletal muscle is dependent on fibre type.J Physiol. 2003 Oct 1;552(Pt 1):213-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.043026. Epub 2003 Jul 14. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12860922 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin and heat shock protein 72 in functionally overloaded rat plantaris muscle.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 May 13;330(3):706-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.049. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15809055
-
Recruitment pattern of muscle fibre type during high intensity exercise (60-100% VO2max) in thoroughbred horses.Res Vet Sci. 2006 Feb;80(1):109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2005.04.006. Epub 2005 Jun 29. Res Vet Sci. 2006. PMID: 15992837 Clinical Trial.
-
Calcineurin and skeletal muscle growth.Proc Nutr Soc. 2004 May;63(2):341-9. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004362. Proc Nutr Soc. 2004. PMID: 15294053 Review.
-
Molecular regulation of individual skeletal muscle fibre types.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Aug;178(4):413-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01158.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12864747 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclosporine immunomodulation retards regeneration of surgically transected corneal nerves.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Feb 13;53(2):732-40. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8445. Print 2012 Feb. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22205605 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Glucose Ingestion Inhibits Endurance Exercise-Induced IL-6 Producing Macrophage Infiltration in Mice Muscle.Nutrients. 2019 Jun 30;11(7):1496. doi: 10.3390/nu11071496. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31262006 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Modulation of Systemic Inflammatory Response to Exhaustive Exercise in Relation to Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 8;9(5):401. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050401. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between signalling pathways involved in skeletal muscle responses to endurance exercise.Pflugers Arch. 2006 May;452(2):125-39. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-0030-9. Epub 2006 Jan 18. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16437222 Review.
-
Changes of myogenic reactive oxygen species and interleukin-6 in contracting skeletal muscle cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:145418. doi: 10.1155/2012/145418. Epub 2012 May 14. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012. PMID: 22666517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agbulut O, Li Z, Mouly V, Butler-Browne GS. Analysis of skeletal and cardiac muscle from desmin knock-out and normal mice by high resolution separation of myosin heavy-chain isoforms. Biol Cell. 1996;88:131–135. - PubMed
-
- Bartoccioni E, Michaelis D, Hohlfeld R. Constitutive and cytokine-induced production of interleukin-6 by human myoblasts. Immunol Lett. 1994;42:135–138. - PubMed
-
- Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Role of calcineurin in striated muscle: development, adaptation, and disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;311:1133–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

