Developmentally induced changes in transcriptional program alter spatial organization across chromosomes
- PMID: 15905407
- PMCID: PMC1132005
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1307205
Developmentally induced changes in transcriptional program alter spatial organization across chromosomes
Abstract
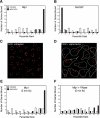
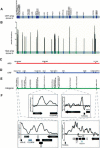
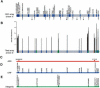
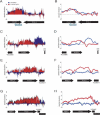
Although the spatial location of genes within the nucleus has been implicated in their transcriptional status, little is known about the dynamics of gene location that accompany large-scale changes in gene expression. The mating of haploid yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is accompanied by a large-scale change in transcription and developmental program. We examined changes in nuclear organization that accompany stimulus by the mating pheromone alpha factor and found that most alpha-factor-induced genes become associated with components of the nuclear envelope. The myosin-like protein Mlp1, which has been implicated in mRNA export, was further shown to exhibit RNA dependence in its association with alpha-factor-induced genes. High-resolution mapping of association of chromosome III with Mlp1 revealed alpha-factor-dependent determinants of nuclear pore association, including origins of replication, specific intergenic regions, and the 3' ends of transcriptionally activated genes. Taken together, these results reveal RNA- and DNA-dependent determinants of nuclear organization as well as a detailed picture of how an entire chromosome alters its spatial conformation in response to a developmental cue.
Figures

References
-
- Aebi M., Clark, M.W., Vijayraghavan, U., and Abelson, J. 1990. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 224: 72–80. - PubMed
-
- Andrulis E.D., Neiman, A.M., Zappulla, D.C., and Sternglanz, R. 1998. Perinuclear localization of chromatin facilitates transcriptional silencing. Nature 394: 592–595. - PubMed
-
- Azuma Y. and Dasso, M. 2000. The role of Ran in nuclear function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12: 302–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
