A relevant in vitro rat model for the evaluation of blood-brain barrier translocation of nanoparticles
- PMID: 15905957
- PMCID: PMC2773840
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-005-5094-3
A relevant in vitro rat model for the evaluation of blood-brain barrier translocation of nanoparticles
Abstract
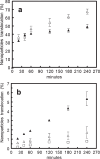
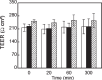
Poly(MePEG2000cyanoacrylate-co-hexadecylcyanoacrylate) (PEG-PHDCA) nanoparticles have demonstrated their capacity to reach the rat central nervous system after intravenous injection. For insight into the transport of colloidal systems across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), we developed a relevant in vitro rat BBB model consisting of a coculture of rat brain endothelial cells (RBECs) and rat astrocytes. The RBECs used in our model displayed and retained structural characteristics of brain endothelial cells, such as expression of P-glycoprotein, occludin and ZO-1, and immunofluorescence studies showed the specific localization of occludin and ZO1. The high values of transendothelial electrical resistance and low permeability coefficients of marker molecules demonstrated the functionality of this model. The comparative passage of polyhexadecylcyanoacrylate and PEG-PHDCA nanoparticles through this model was investigated, showing a higher passage of PEGylated nanoparticles, presumably by endocytosis. This result was confirmed by confocal microscopy. Thanks to a good in vitro/in vivo correlation, this rat BBB model will help in understanding the mechanisms of nanoparticle translocation and in designing new types of colloidal carriers as brain delivery systems.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2009 Mar-Apr;54(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19111869
-
Translocation of poly(ethylene glycol-co-hexadecyl)cyanoacrylate nanoparticles into rat brain endothelial cells: role of apolipoproteins in receptor-mediated endocytosis.Biomacromolecules. 2007 Mar;8(3):793-9. doi: 10.1021/bm060711a. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Biomacromolecules. 2007. PMID: 17309294
-
Establishment of coculture model of blood-brain barrier in vitro for nanoparticle's transcytosis and toxicity evaluation.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Apr;41(4):296-304. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16856472
-
Polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles for delivery of drugs across the blood-brain barrier.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009 Sep-Oct;1(5):463-74. doi: 10.1002/wnan.5. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009. PMID: 20049811 Review.
-
In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier for the study of drug delivery to the brain.Mol Pharm. 2014 Jul 7;11(7):1949-63. doi: 10.1021/mp500046f. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24641309 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of high-resolution imaging in the evaluation of nanosystems for bioactive encapsulation and targeted nanotherapy.Micron. 2007;38(8):804-18. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Micron. 2007. PMID: 17669661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: An overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 May;36(5):862-90. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16630991. Epub 2016 Feb 11. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016. PMID: 26868179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of nanomaterials safety in research environment.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010 Dec 10;7:40. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-7-40. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 21143952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-targeted intranasal delivery of protein-based gene therapy for treatment of ischemic stroke.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 12;14(12):4773-4786. doi: 10.7150/thno.98088. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39239521 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Blood-Brain Barrier Transfer-Strategies and Challenges.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 7;8(10):2003937. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003937. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alyautdin R. N., Tezikov E. B., Ramge P., Kharkevich D. A., Begley D. J., Kreuter J. Significant entry of tubocurarine into the brain of rats by adsorption to polysorbate 80-coated polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles: an in situ brain perfusion study. J. Microencapsul. 1998;15:67–74. doi: 10.3109/02652049809006836. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

