Expression of genes encoding innate host defense molecules in normal human monocytes in response to Candida albicans
- PMID: 15908401
- PMCID: PMC1111842
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3714-3724.2005
Expression of genes encoding innate host defense molecules in normal human monocytes in response to Candida albicans
Abstract
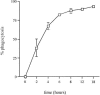
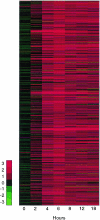
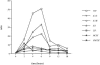
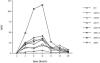
Little is known about the regulation and coordinated expression of genes involved in the innate host response to Candida albicans. We therefore examined the kinetic profile of gene expression of innate host defense molecules in normal human monocytes infected with C. albicans using microarray technology. Freshly isolated peripheral blood monocytes from five healthy donors were incubated with C. albicans for 0 to 18 h in parallel with time-matched uninfected control cells. RNA from monocytes was extracted and amplified for microarray analysis, using a 42,421-gene cDNA chip. Expression of genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6, and leukemia inhibitory factor, was markedly enhanced during the first 6 h and coincided with an increase in phagocytosis. Expression of these genes returned to near baseline by 18 h. Genes encoding chemokines, including IL-8; macrophage inflammatory proteins 1, 3, and 4; and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, also were strongly up-regulated, with peak expression at 4 to 6 h, as were genes encoding chemokine receptors CCR1, CCR5, CCR7, and CXCR5. Expression of genes whose products may protect monocyte viability, such as BCL2-related protein, metallothioneins, CD71, and SOCS3, was up-regulated at 4 to 6 h and remained elevated throughout the 18-h time course. On the other hand, expression of genes encoding T-cell-regulatory molecules (e.g., IL-12, gamma interferon, and transforming growth factor beta) was not significantly affected during the 18-h incubation. Moreover, genes encoding IL-15, the IL-13 receptor (IL-13Ra1), and CD14 were suppressed during the 18-h exposure to C. albicans. Thus, C. albicans is a potent inducer of a dynamic cascade of expression of genes whose products are related to the recruitment, activation, and protection of neutrophils and monocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein A down-regulates proinflammatory cytokine production evoked by Candida albicans in human alveolar macrophages and monocytes.J Immunol. 1999 Oct 15;163(8):4495-502. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10510392
-
IL-4 decreases the expression of the monocyte differentiation marker CD14, paralleled by an increasing accessory potency.Immunobiology. 1991 Aug;182(5):449-64. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80209-3. Immunobiology. 1991. PMID: 1717365
-
Comparison of pathogenesis and host immune responses to Candida glabrata and Candida albicans in systemically infected immunocompetent mice.Infect Immun. 2001 Aug;69(8):5046-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.5046-5055.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11447185 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of TNF-alpha, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 by doxorubicin in human lung carcinoma cells.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;52(5):391-8. doi: 10.1007/s00280-003-0665-1. Epub 2003 Aug 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12908082
-
Role of tumor necrosis factor and colony-stimulating factors in phagocyte function against Candida albicans.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Sep-Oct;13(5):383-6. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90007-i. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990. PMID: 2126496 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cell surface changes in the Candida albicans mitochondrial mutant goa1Δ are associated with reduced recognition by innate immune cells.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Sep;15(9):1572-84. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12135. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23490206 Free PMC article.
-
Early transcriptional response of human monocyte-like THP-1 cells in response to Trichosporon asahii infection.Mycopathologia. 2015 Feb;179(1-2):11-20. doi: 10.1007/s11046-014-9784-y. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Mycopathologia. 2015. PMID: 25179349
-
Genome-wide host RNA signatures of infectious diseases: discovery and clinical translation.Immunology. 2018 Feb;153(2):171-178. doi: 10.1111/imm.12841. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 28921535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential role of hepcidin in host resistance to disseminated candidiasis.Cell Rep. 2025 May 27;44(5):115649. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115649. Epub 2025 May 5. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40333187 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression-based classifiers identify Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice and humans.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e48979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048979. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, W. S. 2002. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:410-416. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, W. S., and D. J. Hilton. 2004. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:503-529. - PubMed
-
- Andriole, V. T. 1999. The 1998 Garrod lecture. Current and future antifungal therapy: new targets for antifungal agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 44:151-162. - PubMed
-
- Ashman, R. B., C. S. Farah, S. Wanasaengsakul, Y. Hu, G. Pang, and R. L. Clancy. 2004. Innate versus adaptive immunity in Candida albicans infection. Immunol. Cell Biol. 82:196-204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

