Formation and properties of hairpin and tetraplex structures of guanine-rich regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes
- PMID: 15908587
- PMCID: PMC1133794
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki606
Formation and properties of hairpin and tetraplex structures of guanine-rich regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes
Abstract
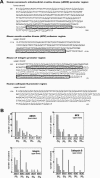
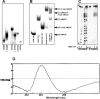
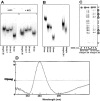
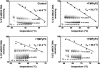
Clustered guanine residues in DNA readily generate hairpin or a variety of tetrahelical structures. The myogenic determination protein MyoD was reported to bind to a tetrahelical structure of guanine-rich enhancer sequence of muscle creatine kinase (MCK) more tightly than to its target E-box motif [K. Walsh and A. Gualberto (1992) J. Biol. Chem., 267, 13714-13718], suggesting that tetraplex structures of regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes could contribute to transcriptional regulation. In the current study we show that promoter or enhancer sequences of various muscle-specific genes display a disproportionately high incidence of guanine clusters. The sequences derived from the guanine-rich promoter or enhancer regions of three muscle-specific genes, human sarcomeric mitochondrial creatine kinase (sMtCK), mouse MCK and alpha7 integrin formed diverse secondary structures. The sMtCK sequence folded into a hairpin structure; the alpha7 integrin oligonucleotide generated a unimolecular tetraplex; and sequences from all three genes associated to generate bimolecular tetraplexes. Furthermore, two neighboring non-contiguous guanine-rich tracts in the alpha7 integrin promoter region also paired to form a tetraplex structure. We also show that homodimeric MyoD bound bimolecular tetraplex structures of muscle-specific regulatory sequences more efficiently than its target E-box motif. These results are consistent with a role of tetrahelical structures of DNA in the regulation of muscle-specific gene expression.
Figures
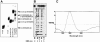

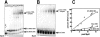
References
-
- Simonsson T. G-quadruplex DNA structures—variations on a theme. Biol. Chem. 2001;382:621–628. - PubMed
-
- Shafer R.H., Smirnov I. Biological aspects of DNA/RNA quadruplexes. Biopolymers. 2000;56:209–227. - PubMed
-
- Parkinson G.N., Lee M.P., Neidle S. Crystal structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA. Nature. 2002;417:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Chang C.C., Kuo I.C., Ling I.F., Chen C.T., Chen H.C., Lou P.J., Lin J.J., Chang T.C. Detection of quadruplex DNA structures in human telomeres by a fluorescent carbazole derivative. Anal. Chem. 2004;76:4490–4494. - PubMed

