Root border-like cells of Arabidopsis. Microscopical characterization and role in the interaction with rhizobacteria
- PMID: 15908608
- PMCID: PMC1150414
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.051813
Root border-like cells of Arabidopsis. Microscopical characterization and role in the interaction with rhizobacteria
Abstract
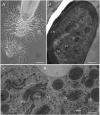
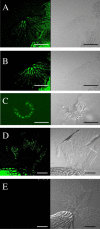
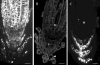
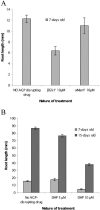
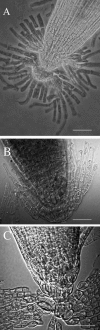
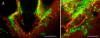
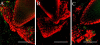
Plant roots of many species produce thousands of cells that are released daily into the rhizosphere. These cells are commonly termed border cells because of their major role in constituting a biotic boundary layer between the root surface and the soil. In this study, we investigated the occurrence and ultrastructure of such cells in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) using light and electron microscopy coupled to high-pressure freezing. The secretion of cell wall molecules including pectic polysaccharides and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs) was examined also using immunofluorescence microscopy and a set of anticarbohydrate antibodies. We show that root tips of Arabidopsis seedlings released cell layers in an organized pattern that differs from the rather randomly dispersed release observed in other plant species studied to date. Therefore, we termed such cells border-like cells (BLC). Electron microscopical results revealed that BLC are rich in mitochondria, Golgi stacks, and Golgi-derived vesicles, suggesting that these cells are actively engaged in secretion of materials to their cell walls. Immunocytochemical data demonstrated that pectins as well as AGPs are among secreted material as revealed by the high level of expression of AGP-epitopes. In particular, the JIM13-AGP epitope was found exclusively associated with BLC and peripheral cells in the root cap region. In addition, we investigated the function of BLC and root cap cell AGPs in the interaction with rhizobacteria using AGP-disrupting agents and a strain of Rhizobium sp. expressing a green fluorescent protein. Our findings demonstrate that alteration of AGPs significantly inhibits the attachment of the bacteria to the surface of BLC and root tip.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fucosylated arabinogalactan-proteins are required for full root cell elongation in arabidopsis.Plant J. 2002 Oct;32(1):105-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01406.x. Plant J. 2002. PMID: 12366804
-
Disruption of arabinogalactan proteins disorganizes cortical microtubules in the root of Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2007 Oct;52(2):240-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03224.x. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Plant J. 2007. PMID: 17672840
-
Localization of an arabinogalactan protein epitope and the effects of Yariv phenylglycoside during zygotic embryo development of Arabidopsis thaliana.Protoplasma. 2006 Nov;229(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s00709-006-0185-z. Epub 2006 Oct 6. Protoplasma. 2006. PMID: 17019527
-
Arabinogalactan proteins in root-microbe interactions.Trends Plant Sci. 2013 Aug;18(8):440-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Trends Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23623239 Review.
-
Arabinogalactan proteins in root and pollen-tube cells: distribution and functional aspects.Ann Bot. 2012 Jul;110(2):383-404. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs143. Ann Bot. 2012. PMID: 22786747 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Root exudate of Solanum tuberosum is enriched in galactose-containing molecules and impacts the growth of Pectobacterium atrosepticum.Ann Bot. 2016 Oct 1;118(4):797-808. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw128. Ann Bot. 2016. PMID: 27390353 Free PMC article.
-
Shedding the Last Layer: Mechanisms of Root Cap Cell Release.Plants (Basel). 2020 Mar 1;9(3):308. doi: 10.3390/plants9030308. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium sp. YAS34 is not necessary for biofilm formation on Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus roots but contributes to root colonization.Environ Microbiol. 2008 Aug;10(8):2150-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01650.x. Epub 2008 May 28. Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18507672 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of arabinogalactan proteins from the root caps of pea and Brassica napus on Aphanomyces euteiches zoospore chemotaxis and germination.Plant Physiol. 2012 Aug;159(4):1658-70. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.198507. Epub 2012 May 29. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22645070 Free PMC article.
-
The Brassicaceae species Heliophila coronopifolia produces root border-like cells that protect the root tip and secrete defensin peptides.Ann Bot. 2017 Mar 1;119(5):803-813. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw141. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 27481828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andème-Onzighi C, Sivaguru M, Judy-March J, Baskin TI, Driouich A (2002) The reb1-1 mutation of Arabidopsis alters the morphology of trichoblasts, the expression of arabinogalactan-proteins and the organization of cortical microtubules. Planta 215: 949–958 - PubMed
-
- Arnon D, Hoagland DR (1940) Crop production in artificial culture solutions and in soils with special reference to factors influencing yields and absorption of organic nutrients. Soil Sci 50: 463–483
-
- Baskin TI, Betzner AS, Hoggart R, Curk A, Williamson RE (1992) Root morphology mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 19: 427–438
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

