Interferon alfacon1 is an inhibitor of SARS-corona virus in cell-based models
- PMID: 15911026
- PMCID: PMC7114208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.01.002
Interferon alfacon1 is an inhibitor of SARS-corona virus in cell-based models
Abstract
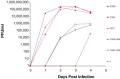
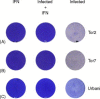
Preliminary data examining interferon alfacon1 treatment of SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome-corona virus)-infected patients suggests this therapy is well tolerated and of therapeutic benefit. We report herein that interferon alfacon1, has potent in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV. In a cytopathic effect protection (CPE) assay, interferon alfacon1 inhibited the generation of CPE in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.001 microg/ml, a clinically achievable level. Furthermore, interferon alfacon1 also demonstrated significant antiviral activity in yield reduction and plaque reduction assays. The in vitro antiviral activity of interferon alfacon1 against SARS-CoV suggests continued evaluation of interferon alfacon1 as a therapeutic treatment for patients infected with SARS-CoV.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potent in vitro activity of the albumin fusion type 1 interferons (albumin-interferon-alpha and albumin-interferon-beta) against RNA viral agents of bioterrorism and the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus.Chemotherapy. 2008;54(3):176-80. doi: 10.1159/000140361. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Chemotherapy. 2008. PMID: 18560223
-
Interferon alfacon 1 inhibits SARS-CoV infection in human bronchial epithelial Calu-3 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Jun 20;371(1):110-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18406349 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus is inhibited by interferon- alpha.J Infect Dis. 2004 Apr 1;189(7):1164-7. doi: 10.1086/382597. Epub 2004 Mar 12. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15031783 Free PMC article.
-
Broad-spectrum coronavirus antiviral drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019 Apr;14(4):397-412. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1581171. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 30849247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitivity of SARS/MERS CoV to interferons and other drugs based on achievable serum concentrations in humans.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2014;14(1):37-43. doi: 10.2174/1871526514666140713152858. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25019238 Review.
Cited by
-
Host Factors in Coronavirus Replication.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018;419:1-42. doi: 10.1007/82_2017_25. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28643204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a high-throughput screen for inhibitors of SARS CoV and its application in screening of a 100,000-compound library.J Biomol Screen. 2007 Feb;12(1):33-40. doi: 10.1177/1087057106296688. Epub 2006 Dec 22. J Biomol Screen. 2007. PMID: 17200104 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of novel β coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-α2b and ribavirin.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1686. doi: 10.1038/srep01686. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23594967 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus as an agent of emerging and reemerging infection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007 Oct;20(4):660-94. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00023-07. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17934078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-dose intranasal administration with mDEF201 (adenovirus vectored mouse interferon-alpha) confers protection from mortality in a lethal SARS-CoV BALB/c mouse model.Antiviral Res. 2011 Jan;89(1):75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.11.007. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 21093489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basler C.F., Garcia-Sastre A. Viruses and the type I interferon antiviral system: induction and evasion. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2002;21:305–337. - PubMed
-
- Blatt L.M., Davis J.M., Klein S.B., Taylor M.W. The biologic activity and molecular characterization of a novel synthetic interferon-alpha species, consensus interferon. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996;16:489–499. - PubMed
-
- Booth C.M., Matukas L.M., Tomlinson G.A., Rachlis A.R., Rose D.B., Dwosh H.A., Walmsley S.L., Mazzulli T., Avendano M., Derkach P., Ephtimios I.E., Kitai I., Mederski B.D., Shadowitz S.B., Gold W.L., Hawryluck L.A., Rea E., Chenkin J.S., Cescon D.W., Poutanen S.M., Detsky A.S. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003;289:2801–2809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

