In vivo characterization of the nonessential budding yeast anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome components Swm1p, Mnd2p and Apc9p
- PMID: 15911580
- PMCID: PMC1451159
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.040105
In vivo characterization of the nonessential budding yeast anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome components Swm1p, Mnd2p and Apc9p
Abstract
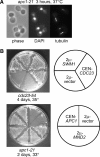
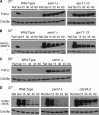
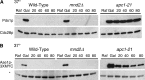
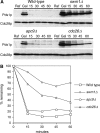
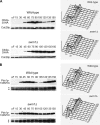
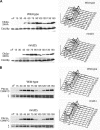
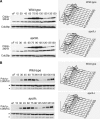
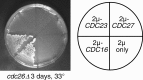
We have examined the in vivo requirement of two recently identified nonessential components of the budding yeast anaphase-promoting complex, Swm1p and Mnd2p, as well as that of the previously identified subunit Apc9p. swm1Delta mutants exhibit synthetic lethality or conditional synthetic lethality with other APC/C subunits and regulators, whereas mnd2Delta mutants are less sensitive to perturbation of the APC/C. swm1Delta mutants, but not mnd2Delta mutants, exhibit defects in APC/C substrate turnover, both during the mitotic cell cycle and in alpha-factor-arrested cells. In contrast, apc9Delta mutants exhibit only minor defects in substrate degradation in alpha-factor-arrested cells. In cycling cells, degradation of Clb2p, but not Pds1p or Clb5p, is delayed in apc9Delta. Our findings suggest that Swm1p is required for full catalytic activity of the APC/C, whereas the requirement of Mnd2p for APC/C function appears to be negligible under standard laboratory conditions. Furthermore, the role of Apc9p in APC/C-dependent ubiquitination may be limited to the proteolysis of a select number of substrates.
Figures






References
-
- Amon, A., 2001. Together until separin do us part. Nat. Cell Biol. 3 E12–E14. - PubMed
-
- Amon, A., S. Irniger and K. Nasmyth, 1994. Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell 77 1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Bachmair, A., D. Finley and A. Varshavsky, 1986. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science 234 179–186. - PubMed
-
- Bloecher, A., G. M. Venturi and K. Tatchell, 2000. Anaphase spindle position is monitored by the BUB2 checkpoint. Nat. Cell Biol. 2 556–558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

