ExsE, a secreted regulator of type III secretion genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 15911752
- PMCID: PMC1142391
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503005102
ExsE, a secreted regulator of type III secretion genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
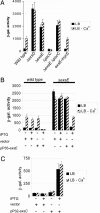
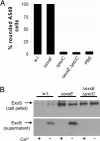
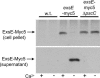
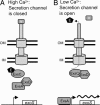
Type III secretion systems are toxin delivery systems that are present in a large number of pathogens. A hallmark of all type III secretion systems studied to date is that expression of one or more of their components is induced upon cell contact. It has been proposed that this induction is controlled by a negative regulator that is itself secreted by means of the type III secretion machinery. Although candidate proteins for this negative regulator have been proposed in a number of systems, for the most part, a direct demonstration of their role in regulation is lacking. Here, we report the discovery of ExsE, a negative regulator of type III secretion gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Deletion of exsE deregulates expression of the type III secretion genes. We provide evidence that ExsE is itself secreted by means of the type III secretion machinery and physically interacts with ExsC, a positive regulator of the type III secretion regulon. Taken together, these data demonstrate that ExsE is the secreted negative regulator that couples triggering of the type III secretion machinery to induction of the type III secretion genes.
Figures



References
-
- Nemunaitis, J., Buckner, C. D., Dorsey, K. S., Willis, D., Meyer, W. & Appelbaum, F. (1998) Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 341–346. - PubMed
-
- Velasco, E., Thuler, L. C., Martins, C. A., Dias, L. M. & Goncalves, V. M. (1997) Am. J. Infect. Control 25, 458–462. - PubMed
-
- Carratala, J., Roson, B., Fernandez-Sevilla, A., Alcaide, F. & Gudiol, F. (1998) Arch. Intern. Med. 158, 868–872. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, K. H., Leung, S. L., Hoekman, H. W., Beekhuis, W. H., Mulder, P. G., Geerards, A. J. & Kijlstra, A. (1999) Lancet 354, 181–185. - PubMed
-
- Beers, S. L. & Abramo, T. J. (2004) Pediatr. Emerg. Care 20, 250–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

