Nephropathy induced by contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors and preventive strategies
- PMID: 15911862
- PMCID: PMC557983
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.1040847
Nephropathy induced by contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors and preventive strategies
Erratum in
- CMAJ. 2005 Nov 8;173(10):1210
Abstract
With the increasing use of contrast media in diagnostic and interventional procedures, nephropathy induced by contrast media has become the third leading cause of hospital-acquired acute renal failure. It is also associated with a significant risk of morbidity and death. The current understanding of the pathogenesis indicates that contrast-medium nephropathy is caused by a combination of renal ischemia and direct toxic effects on renal tubular cells. Patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus and congestive heart failure are at highest risk. Risk factors also include the type and amount of contrast medium administered. Therapeutic prevention strategies are being extensively investigated, but there is still no definitive answer. In this article, we review the current evidence on the causes, pathogenesis and clinical course of contrast-medium nephropathy as well as therapeutic approaches to its prevention evaluated in clinical trials.
Figures

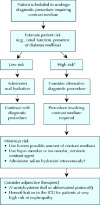
References
-
- Rich MW, Crecelius CA. Incidence, risk factors and clinical course of acute renal insufficiency after cardiac catheterization in patients 70 years of age or older: a prospective study. Arch Intern Med 1990;150:1237-42. - PubMed
-
- Cox CD, Tsikouris JP. Preventing contrast nephropathy: what is the best strategy? A review of the literature. J Clin Pharmacol 2004;44:327-37. - PubMed
-
- Brezis M, Epstein F.H. A closer look at radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. N Engl J Med 1989;320:179-81. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Wolyn R, Rocher LL, Levin RN, O'Neill WW. Acute renal failure after coronary intervention: incidence, risk factors, and relationship to mortality. Am J Med 1997;103:368-75. - PubMed
-
- Rihal CS, Textor SC, Grill DE, Berger PB, Ting HH, Best PJ, et al. Incidence and prognostic importance of acute renal failure after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation 2002;105: 2259-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
