Tyrosine kinase - Role and significance in Cancer
- PMID: 15912202
- PMCID: PMC1074718
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.1.101
Tyrosine kinase - Role and significance in Cancer
Abstract
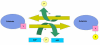
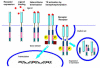
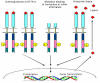
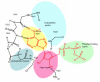
Tyrosine kinases are important mediators of the signaling cascade, determining key roles in diverse biological processes like growth, differentiation, metabolism and apoptosis in response to external and internal stimuli. Recent advances have implicated the role of tyrosine kinases in the pathophysiology of cancer. Though their activity is tightly regulated in normal cells, they may acquire transforming functions due to mutation(s), overexpression and autocrine paracrine stimulation, leading to malignancy. Constitutive oncogenic activation in cancer cells can be blocked by selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors and thus considered as a promising approach for innovative genome based therapeutics. The modes of oncogenic activation and the different approaches for tyrosine kinase inhibition, like small molecule inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, heat shock proteins, immunoconjugates, antisense and peptide drugs are reviewed in light of the important molecules. As angiogenesis is a major event in cancer growth and proliferation, tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a target for anti-angiogenesis can be aptly applied as a new mode of cancer therapy. The review concludes with a discussion on the application of modern techniques and knowledge of the kinome as means to gear up the tyrosine kinase drug discovery process.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

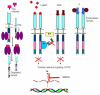
References
-
- Hunter T. Signaling-2000 and Beyond. Cell. 2000;100:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Cell Signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2000;103:211–225. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Hunter T, Cooper JA. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, King LJr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preperations in vitro. Nature. 1978;276:409–410. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

