Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA
- PMID: 159130
- PMCID: PMC1931615
- DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90049-7
Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA
Abstract
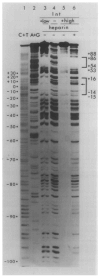
We have studied the interaction of highly purified Int protein with DNA restriction fragments from the lambda phage attachment site (attP) region. Two different DNA sequences are protected by bound Int protein against partial digestion by either pancreatic DNAase or neocarzinostatin. One Int binding site includes the 15 bp common core sequence (the crossover region for site-specific recombination) plus several bases of sequence adjoining the core in both the P and P' arms. The second Int-protected site occurs 70 bp to the right of the common core in the P' arm, just at the distal end of the sequence encoding Int protein. The two Int binding sites are of comparable size, 30-35 bp, but do not share any extensive sequence homology. The interaction of Int with the two sites is distinctly different, as defined by the observation that only the site in the P' arm and not the site at the common core region is protected by Int in the face of challenge by the polyanion heparin. Restriction fragments containing DNA from the bacterial attachment site (attB) region exhibit a different pattern of interaction with Int. In the absence of heparin, a smaller (15 bp) sequence, which includes the left half of the common core region and the common core-B arm juncture, is protected against nuclease digestion by Int protein. No sequences from this region are protected by Int in the presence of heparin.
Figures

 ) (see Figure 5 and Discussion). The bottom strand corresponds to the Int message. Two restriction fragments from the attP region were used: one, Hinf I (−114)-Mbo II (+173), was labeled with 32P (*) at the Hinf I site at the 5′ end of the top strand (* ‒ ‒ →); the second, Hinf I (−114)-Mnl I (+115) (← ‒ ‒ *), was labeled at the Mnl I site at the 5′ end of the bottom strand. The attB restriction fragment Hpa II (−43)-Hha I (+80) was labeled at the Hpa II site at the 5′ end of the top strand (see Experimental Procedures).
) (see Figure 5 and Discussion). The bottom strand corresponds to the Int message. Two restriction fragments from the attP region were used: one, Hinf I (−114)-Mbo II (+173), was labeled with 32P (*) at the Hinf I site at the 5′ end of the top strand (* ‒ ‒ →); the second, Hinf I (−114)-Mnl I (+115) (← ‒ ‒ *), was labeled at the Mnl I site at the 5′ end of the bottom strand. The attB restriction fragment Hpa II (−43)-Hha I (+80) was labeled at the Hpa II site at the 5′ end of the top strand (see Experimental Procedures).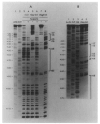


 ) Inverted repeat; (
) Inverted repeat; (
 ) palindromic sequences. Less well protected bases in NCS experiments with the top strand (▼); or the bottom strand (▲) (see Results).
) palindromic sequences. Less well protected bases in NCS experiments with the top strand (▼); or the bottom strand (▲) (see Results).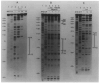
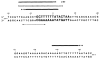
 ) sequences protected from micrococcal nuclease. All experiments were carried out with a fragment labeled in the top strand (see Figures 1 and 6). (●), (○) or (
) sequences protected from micrococcal nuclease. All experiments were carried out with a fragment labeled in the top strand (see Figures 1 and 6). (●), (○) or (
 ) Bases whose extent of protection is not known; see legend to Figure 5 and Results. (
) Bases whose extent of protection is not known; see legend to Figure 5 and Results. (
 ) A palindromic sequence.
) A palindromic sequence.References
-
- Bernardi A, Gaillard C, Bernardi G. The specificity of five DNAases as studied by the analysis of 5′-terminal doublets. Eur J Biochem. 1975;52:451–457. - PubMed
-
- Bidwell K, Landy A. Structural features of λ site-specific recombination at a secondary att site in ga/T. Cell. 1979;16:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Campbell A, Heffernan L, Hu S-L, Szybalski W. The integrase promoter of bacteriophage lambda. In: Bukhari AI, Shapiro JA, Adhya SL, editors. DNA Insertion Elements, Plasmids, and Episomes. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1977. pp. 375–379.
-
- Chamberlin MJ. RNA polymerase—an overview. In: Losick R, Chamberlin M, editors. RNA Polymerase. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1976. pp. 35–37.
-
- Christie GE, Platt T. A secondary attachment site for bacteriophage λ in trpC of E. coli. Cell. 1979;16:407–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

