Increased duodenal iron uptake and transfer in a rat model of chronic hypoxia is accompanied by reduced hepcidin expression
- PMID: 15914574
- PMCID: PMC1774692
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.062083
Increased duodenal iron uptake and transfer in a rat model of chronic hypoxia is accompanied by reduced hepcidin expression
Abstract
Background: Despite the requirement for increased iron delivery for erythropoiesis during hypoxia, there is very little information on how duodenal iron uptake and its transfer to the blood adapts to this condition.
Aims: To assess the effects of 30 days of chronic hypoxia in rats on luminal iron uptake and transfer of the metal to blood, together with gene expression of hepcidin, a proposed negative regulator of iron transport.
Methods: 59-Fe uptake by isolated duodenum and its transfer to blood by in vivo duodenal segments was measured after exposure of rats to room air or 10% oxygen for four weeks. Liver hepcidin expression was measured by real time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The effects of hypoxia on hepcidin gene expression by HepG2 cells was also determined.
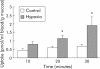
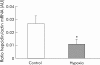
Results: Hypoxia did not affect villus length but enhanced (+192.6%) luminal iron uptake by increasing the rate of uptake by all enterocytes, particularly those on the upper villus. Hypoxia promoted iron transfer to the blood but reduced mucosal iron accumulation in vivo by 66.7%. Hypoxia reduced expression of hepcidin mRNA in both rat liver and HepG2 cells.
Conclusions: Prolonged hypoxia enhances iron transport from duodenal lumen to blood but the process is unable to fully meet the iron requirement for increased erythropoiesis. Reduced secretion of hepcidin may be pivotal to the changes in iron absorption. The processes responsible for suppression of hepcidin expression are unknown but are likely to involve a direct effect of hypoxia on hepatocytes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepcidin expression inversely correlates with the expression of duodenal iron transporters and iron absorption in rats.Gastroenterology. 2002 Sep;123(3):835-44. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.35353. Gastroenterology. 2002. PMID: 12198710
-
Effect of erythropoietin on hepcidin, DMT1 with IRE, and hephaestin gene expression in duodenum of rats.J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(2):136-43. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2138-5. Epub 2008 Feb 29. J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18306987
-
Iron metabolism in hepcidin1 knockout mice in response to phenylhydrazine-induced hemolysis.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2012 Aug 15;49(2):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 May 19. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22609087
-
Iron-sensing proteins that regulate hepcidin and enteric iron absorption.Annu Rev Nutr. 2010 Aug 21;30:149-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.012809.104801. Annu Rev Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20415583 Review.
-
[Regulation of body iron homeostasis by hepcidin].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2004 Mar 8;58:65-73. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2004. PMID: 15069380 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Chronic hypoxia for the adaptation of extracellular vesicle phenotype.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73453-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39448620 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic hypoxia-inducible factor-2 down-regulates hepcidin expression in mice through an erythropoietin-mediated increase in erythropoiesis.Haematologica. 2012 Jun;97(6):827-34. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.056119. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22207682 Free PMC article.
-
Interrelationships between tissue iron status and erythropoiesis during postweaning development following neonatal iron deficiency in rats.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):G470-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00463.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21193529 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding complexity in the HIF signaling pathway using systems biology and mathematical modeling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Apr;94(4):377-90. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1383-6. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26821588 Review.
-
Hypobaric hypoxia induces iron mobilization from liver and spleen and increases serum iron via activation of ghrelin/GHSR1a/MAPK signalling pathway in mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 20;13(1):20254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47596-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37985861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reynafarje C, Ramos J. Influence of altitude changes on intestinal iron absorption. J Lab Clin Med 1961;57:848–55. - PubMed
-
- Osterloh KR, Simpson RJ, Snape S, et al. Intestinal iron absorption and mucosal transferrin in rats subjected to hypoxia. Blut 1987;55:421–31. - PubMed
-
- Raja KB, Bjarnason I, Simpson RJ, et al. In vitro measurements and adaptive response of Fe2+ uptake by mouse intestine. Cell Biochem Function 1986;5:69–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
