Expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases
- PMID: 15917419
- PMCID: PMC1770676
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2004.022590
Expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases
Abstract
Background: Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) transmits signals from the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) and insulin receptor (IR) and has been associated with the pathogenesis of cancer. IRS-1 downregulation has been suggested to play a role in breast cancer progression, but no simultaneous assessments of IRS-1 expression in primary breast cancer and metastases have been performed.
Aims: To assess IRS-1 expression in primary and metastatic breast cancer.
Methods: IRS-1 expression was analysed by means of immunohistochemistry in 109 samples of primary breast cancer and in 42 matched primary and metastatic tumours. In addition, IRS-1 expression was correlated with selected clinicopathological features, including oestrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and proliferation marker Ki-67 status.
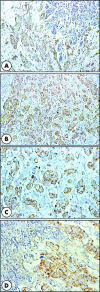
Results: Positive cytoplasmic IRS-1 immunostaining was found in 69.7% (76 of 109) and 76.2% (32 of 42) of the primary and metastatic tumours, respectively. Both IRS-1 positive and IRS-1 negative primary tumours produced IRS-1 positive and IRS-1 negative metastases. IRS-1 expression in primary tumours correlated with poorly differentiated (G3) breast cancer (p < 0.005) and with lymph node involvement (p <0.05). In the subgroup of ERalpha positive primary tumours, IRS-1 expression positively correlated with Ki-67 (p < 0.02, r = 0.351), but in the subgroup of ERalpha negative primary tumours there was a negative correlation (p < 0.03, r = -0.509). IRS-1 expression in lymph node metastases correlated with neither ERalpha nor Ki-67.
Conclusions: IRS-1 might be involved in breast cancer progression. Knowledge about differences between primary and metastatic tumours might help to understand mechanisms of breast cancer progression and lead to the development of more effective anticancer drugs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of nuclear insulin receptor substrate 1 in breast cancer.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Jun;60(6):633-41. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.039107. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 16882697 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ERalpha, ERbeta and Ki-67 in primary tumors and lymph node metastases in breast cancer.Oncol Rep. 2004 Apr;11(4):753-9. Oncol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15010868
-
Expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in primary breast cancer and lymph node metastases: correlations with estrogen receptors alpha and beta.Horm Metab Res. 2003 Nov-Dec;35(11-12):794-801. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-814152. Horm Metab Res. 2003. PMID: 14710360
-
Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep;23(3):385-94. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15595626 Review.
-
Divergent roles for IRS-1 and IRS-2 in breast cancer metastasis.Cell Cycle. 2007 Mar 15;6(6):631-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.6.3987. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17361103 Review.
Cited by
-
IRS1 is highly expressed in localized breast tumors and regulates the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy, while IRS2 is highly expressed in invasive breast tumors.Cancer Lett. 2013 Sep 28;338(2):239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.03.030. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23562473 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IGF1R pathway in cancer with microRNAs: How close are we?RNA Biol. 2018 Mar 4;15(3):320-326. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1338240. Epub 2018 Feb 1. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28613101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) promotes mammary tumor metastasis.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9338-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01032-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030605 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of nuclear insulin receptor substrate 1 in breast cancer.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Jun;60(6):633-41. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.039107. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 16882697 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1 may play divergent roles in human colorectal cancer development and progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 28;26(28):4140-4150. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4140. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32821075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morelli C, Garofalo C, Bartucci M, et al. Estrogen receptor-α regulates the degradation of insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2003;22:4007–16. - PubMed
-
- Yenush L, White MF. The IRS-signalling system during insulin and cytokine action. Bioessays 1997;19:491–500. - PubMed
-
- Burks DJ, White MF. IRS proteins and beta-cell function. Diabetes 2001;1:140–5. - PubMed
-
- Reiss K, Wang JY, Romano G, et al. IGF-I receptor signaling in a prostatic cancer cell line with a PTEN mutation. Oncogene 2000;19:2687–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
