Combination of antimicrobial and endotoxin-neutralizing activities of novel oleoylamines
- PMID: 15917526
- PMCID: PMC1140490
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.6.2307-2313.2005
Combination of antimicrobial and endotoxin-neutralizing activities of novel oleoylamines
Abstract
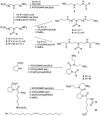
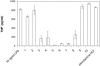
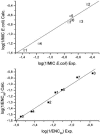
A combination of antimicrobial and endotoxin-neutralizing activities is desired in order to prevent progression from infection to sepsis due to the release of lipopolysaccharide from dying gram-negative bacteria. Lipopolyamines have emerged as a new type of endotoxin-neutralizing compound, but their antimicrobial activity has not been investigated. We synthesized a series of 10 oleoylamines differing in the polyamino head group, particularly in the number and separation between nitrogen atoms and the position of the oleoyl moiety. Compounds showed activity against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria in the micromolar range. Compounds were able to provide penetration of ethidium bromide into bacteria, indicating effects on the bacterial membrane. Oleoylamines neutralized endotoxin in Limulus amoebocyte lysate assays and by neutralization of tumor necrosis factor alpha release in human blood. Comparison of biological activities of compounds identified structural properties responsible for antimicrobial activity, and quantitative structure-property relationship analysis provided a quantitative model for prediction of activity of oleoylamines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of the hydrophobicity to net positive charge ratio on antibacterial and anti-endotoxin activities of structurally similar antimicrobial peptides.Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9;49(5):853-61. doi: 10.1021/bi900724x. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20058937
-
Antimicrobial activity, bactericidal mechanism and LPS-neutralizing activity of the cell-penetrating peptide pVEC and its analogs.J Pept Sci. 2011 Dec;17(12):812-7. doi: 10.1002/psc.1408. Epub 2011 Sep 29. J Pept Sci. 2011. PMID: 21956793
-
Dependence on size and shape of non-nature amino acids in the enhancement of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) neutralizing activities of antimicrobial peptides.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Jan 1;533:492-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.042. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 30176540
-
Mechanisms of endotoxin neutralization by synthetic cationic compounds.J Endotoxin Res. 2006;12(5):261-77. doi: 10.1179/096805106X118852. J Endotoxin Res. 2006. PMID: 17059690 Review.
-
Endotoxin neutralizing peptides.Curr Top Med Chem. 2004;4(11):1173-84. doi: 10.2174/1568026043388079. Curr Top Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15279607 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Signalling in Chronic Inflammation.Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2022 Feb 8;6:24705470221076390. doi: 10.1177/24705470221076390. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2022. PMID: 35155966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural correlates of antibacterial and membrane-permeabilizing activities in acylpolyamines.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Mar;50(3):852-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.3.852-861.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16495242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asseline, U., M. Chassignol, J. Draus, M. Durand, and J. C. Maurizot. 2003. Synthesis and properties of oligo-2′-deoxyribonucleotides containing internucleotidic phosphoramidate linkages modified with pendant groups ending with either two amino or two hydroxyl functions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 11:3499-3511. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, A. T. 1982. Highly discriminating distance based topological index. Chem. Phys. Lett. 89:399-404.
-
- Blagbrough, I. S., A. J. Geall, and S. A. David. 2000. Lipopolyamines incorporating the tetraamine spermine, bound to an alkyl chain, sequester bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10:1959-1962. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, J. 2002. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 420:885-891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

