Normal microRNA maturation and germ-line stem cell maintenance requires Loquacious, a double-stranded RNA-binding domain protein
- PMID: 15918770
- PMCID: PMC1141267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030236
Normal microRNA maturation and germ-line stem cell maintenance requires Loquacious, a double-stranded RNA-binding domain protein
Abstract
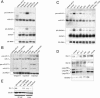
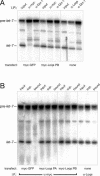
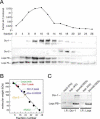
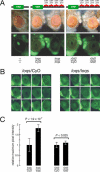
microRNAs (miRNAs) are single-stranded, 21- to 23-nucleotide cellular RNAs that control the expression of cognate target genes. Primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcripts are transformed to mature miRNA by the successive actions of two RNase III endonucleases. Drosha converts pri-miRNA transcripts to precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA); Dicer, in turn, converts pre-miRNA to mature miRNA. Here, we show that normal processing of Drosophila pre-miRNAs by Dicer-1 requires the double-stranded RNA-binding domain (dsRBD) protein Loquacious (Loqs), a homolog of human TRBP, a protein first identified as binding the HIV trans-activator RNA (TAR). Efficient miRNA-directed silencing of a reporter transgene, complete repression of white by a dsRNA trigger, and silencing of the endogenous Stellate locus by Suppressor of Stellate, all require Loqs. In loqs(f00791) mutant ovaries, germ-line stem cells are not appropriately maintained. Loqs associates with Dcr-1, the Drosophila RNase III enzyme that processes pre-miRNA into mature miRNA. Thus, every known Drosophila RNase-III endonuclease is paired with a dsRBD protein that facilitates its function in small RNA biogenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Processing of pre-microRNAs by the Dicer-1-Loquacious complex in Drosophila cells.PLoS Biol. 2005 Jul;3(7):e235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030235. Epub 2005 May 24. PLoS Biol. 2005. PMID: 15918769 Free PMC article.
-
Functional anatomy of the Drosophila microRNA-generating enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28373-28378. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705208200. Epub 2007 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17666393
-
Dicer-1, but not Loquacious, is critical for assembly of miRNA-induced silencing complexes.RNA. 2007 Dec;13(12):2324-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.723707. Epub 2007 Oct 10. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17928574 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Loquacious speaks out.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 9;15(15):R603-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.044. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16085484 Review.
-
The double-stranded microRNA precursor.Postepy Biochem. 2024 May 23;70(1):57-61. doi: 10.18388/pb.2021_522. Print 2024 May 23. Postepy Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39016229 Review.
Cited by
-
Biogenesis of mammalian microRNAs: a global view.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012 Oct;10(5):239-45. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23200133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation repression in human cells by microRNA-induced gene silencing requires RCK/p54.PLoS Biol. 2006 Jul;4(7):e210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040210. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 16756390 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA?RNA. 2005 Dec;11(12):1753-61. doi: 10.1261/rna.2248605. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16314451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conservation of Differential Animal MicroRNA Processing by Drosha and Dicer.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 3;8:730006. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.730006. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35047552 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer partner protein tunes the length of miRNAs using base-mismatch in the pre-miRNA stem.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Apr 20;46(7):3726-3741. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky043. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29373753 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

