High-resolution ultrahigh-field MRI of stroke
- PMID: 15919599
- PMCID: PMC2031925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2005.02.010
High-resolution ultrahigh-field MRI of stroke
Abstract
Background: Ultrahigh-field MRI at 8 T offers unprecedented resolution for imaging brain structures and microvasculature.
Objective: The aim of this study is to apply high-resolution MRI for stroke imaging and to characterize findings at 1.5 and 8 T.
Methods: Seventeen subjects with minor ischemic infarcts were studied using T2-weighted gradient echo (GE) and rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement (RARE) images at 8 T with resolution up to 200 microm. In 10 subjects, T1- and T2-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images were also acquired at 1.5-T MRI.
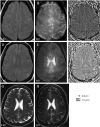
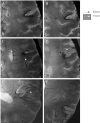
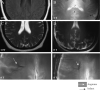
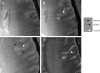
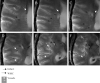
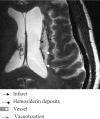
Results: The 8-T images showed infarcts as sharply demarcated areas of high-signal intensity (n=21) and revealed more infarctions than 1.5-T images (n=14) (P<.003). The low-signal intensity areas that surrounded infarctions were suggestive of hemosiderin deposits. The 8-T characteristics of microvessels terminating within the infractions were distinct from normal vasculature. The 8-T images revealed an angioma at the site of a second stroke, not apparent on 1.5-T images.
Conclusions: Ultrahigh-field MRI at 8 T is feasible for stroke imaging. The 8-T MRI visualized infarcts and microvasculature with high resolution, revealing infarcts and vascular pathologies that were not apparent at 1.5 T.
Figures

References
-
- Dobson J. Magnetic iron compounds in neurological disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1012:183–92. - PubMed
-
- deGroot JC, de Leeuw FE, Ouderk M, Hofman A, Jolles J, Breteler MM. Cerebral white matter lesions and subjective cognitive dysfunction: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Neurology. 2001;56:1539–41. - PubMed
-
- Wahlund LO, Barkhof F, Fazekas F, Bronge L, Augustin M, Sjogren M, et al. A new rating scale for age-related white matter changes applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke. 2001;32:1318–22. - PubMed
-
- Marstrand JR, Garde E, Rostrup E, Ring P, Rosenbaum S, Mortensen EL, et al. Cerebral perfusion and cerebrovascular reactivity are reduced in white matter hyperintensities. Stroke. 2002;34:972–6. - PubMed
-
- Pantoni L, Garcia JH. Pathogenesis of leukoaraoisis: a review. Stroke. 1997;28:652–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

