A functional glutamatergic neurone network in the medial septum and diagonal band area
- PMID: 15919710
- PMCID: PMC1464770
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089664
A functional glutamatergic neurone network in the medial septum and diagonal band area
Abstract
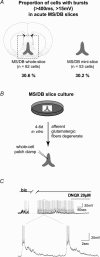
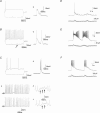
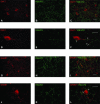
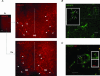
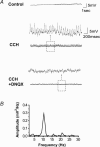
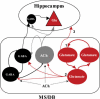
The medial septum and diagonal band complex (MS/DB) is important for learning and memory and is known to contain cholinergic and GABAergic neurones. Glutamatergic neurones have also been recently described in this area but their function remains unknown. Here we show that local glutamatergic neurones can be activated using 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and the GABA(A) receptor antagonist bicuculline in regular MS/DB slices, or mini-MS/DB slices. The spontaneous glutamatergic responses were mediated by AMPA receptors and, to a lesser extend, NMDA receptors, and were characterized by large, sometimes repetitive activity that elicited bursts of action potentials postsynaptically. Similar repetitive AMPA receptor-mediated bursts were generated by glutamatergic neurone activation within the MS/DB in disinhibited organotypic MS/DB slices, suggesting that the glutamatergic responses did not originate from extrinsic glutamatergic synapses. It is interesting that glutamatergic neurones were part of a synchronously active network as large repetitive AMPA receptor-mediated bursts were generated concomitantly with extracellular field potentials in intact half-septum preparations in vitro. Glutamatergic neurones appeared important to MS/DB activation as strong glutamatergic responses were present in electrophysiologically identified putative cholinergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic neurones. In agreement with this, we found immunohistochemical evidence that vesicular glutamate-2 (VGLUT2)-positive puncta were in proximity to choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-, glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67)- and VGLUT2-positive neurones. Finally, MS/DB glutamatergic neurones could be activated under more physiological conditions as a cholinergic agonist was found to elicit rhythmic AMPA receptor-mediated EPSPs at a theta relevant frequency of 6-10 Hz. We propose that glutamatergic neurones within the MS/DB can excite cholinergic and GABAergic neurones, and that they are part of a connected excitatory network, which upon appropriate activation, may contribute to rhythm generation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glutamatergic neurons of the mouse medial septum and diagonal band of Broca synaptically drive hippocampal pyramidal cells: relevance for hippocampal theta rhythm.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 24;30(47):15951-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3663-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21106833 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and role of Kv3.1b in neurons in the medial septum diagonal band complex.Neuroscience. 2010 Mar 31;166(3):952-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.020. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20083165
-
Distinct electrophysiological properties of glutamatergic, cholinergic and GABAergic rat septohippocampal neurons: novel implications for hippocampal rhythmicity.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 15;551(Pt 3):927-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.046847. Epub 2003 Jul 15. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12865506 Free PMC article.
-
Pacemaker neurons of the forebrain medical septal area and theta rhythm of the hippocampus.Membr Cell Biol. 1998;11(6):715-25. Membr Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9718568 Review.
-
Effects of vasopressin and related peptides on neurons of the rat lateral septum and ventral hippocampus.Prog Brain Res. 1998;119:285-310. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61576-9. Prog Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 10074795 Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamatergic neurons of the mouse medial septum and diagonal band of Broca synaptically drive hippocampal pyramidal cells: relevance for hippocampal theta rhythm.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 24;30(47):15951-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3663-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21106833 Free PMC article.
-
The nicotinic receptor blocker hexamethonium alters neuronal responses to glutamate in the medial septal area of the brain of the ground squirrel in vitro.Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2008 Mar;38(3):297-307. doi: 10.1007/s11055-008-0042-y. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18264777
-
GABAergic neurons of the medial septum play a nodal role in facilitation of nociception-induced affect.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 21;5:15419. doi: 10.1038/srep15419. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26487082 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cholinergic and GABAergic medial septal/diagonal band cell populations in the emergence of diencephalic amnesia.Neuroscience. 2009 Apr 21;160(1):32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.02.044. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19264109 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal non-theta state: The "Janus face" of information processing.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Mar 7;17:1134705. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1134705. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 36960401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso A, Gaztelu JM, Buno W, JR, Garcia-Austt E. Cross-correlation analysis of septohippocampal neurons during theta-rhythm. Brain Res. 1987;413:135–146. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Kurz J. An analysis of the origins of the cholinergic and noncholinergic septal projections to the hippocampal formation of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985;240:37–59. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong JN, MacVicar BA. Theta-frequency facilitation of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the principal cells of the medial septum. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:1709–1718. - PubMed
-
- Avoli M, D'Antuono M, Louvel J, Kohling R, Biagini G, Pumain R, D'Arcangelo G, Tancredi V. Network and pharmacological mechanisms leading to epileptiform synchronization in the limbic system in vitro. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:167–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

