Splicing potentiation by growth factor signals via estrogen receptor phosphorylation
- PMID: 15919818
- PMCID: PMC1149443
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503197102
Splicing potentiation by growth factor signals via estrogen receptor phosphorylation
Abstract
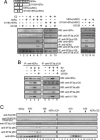
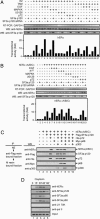
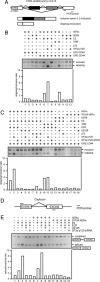
Mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated growth factor signals are known to augment the ligand-induced transactivation function of nuclear estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) through phosphorylation of Ser-118 within the ERalpha N-terminal transactivation (activation function-1) domain. We identified the spliceosome component splicing factor (SF)3a p120 as a coactivator specific for human ERalpha (hERalpha) activation function-1 that physically associated with ERalpha dependent on the phosphorylation state of Ser-118. SF3a p120 potentiated hERalpha-mediated RNA splicing, and notably, the potentiation of RNA splicing by SF3a p120 depended on hER Ser-118 phosphorylation. Thus, our findings suggest a mechanism by which growth factor signaling can regulate gene expression through the modulation of RNA splicing efficiency via phosphorylation of sequence-specific activators, after association between such activators and the spliceosome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-function analysis of the U2 snRNP-associated splicing factor SF3a.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Jun;33(Pt 3):439-42. doi: 10.1042/BST0330439. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 15916536 Review.
-
In vivo potentiation of human oestrogen receptor alpha by Cdk7-mediated phosphorylation.Genes Cells. 2004 Oct;9(10):983-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2004.00777.x. Genes Cells. 2004. Retraction in: Genes Cells. 2013 Dec;18(12):1144. PMID: 15461668 Retracted.
-
Regulation of human estrogen receptor alpha-mediated gene transactivation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by human coactivator and corepressor proteins.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Feb;103(2):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.11.001. Epub 2006 Dec 27. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17194583
-
Specific inhibition of serine- and arginine-rich splicing factors phosphorylation, spliceosome assembly, and splicing by the antitumor drug NB-506.Cancer Res. 2001 Sep 15;61(18):6876-84. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11559564
-
Estrogen receptor-mediated cross-talk with growth factor signaling pathways.Breast Cancer. 2001;8(1):3-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02967472. Breast Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11180760 Review.
Cited by
-
Liganded and unliganded activation of estrogen receptor and hormone replacement therapies.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1812(8):1054-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 May 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21605666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinases and protein phosphorylation as regulators of steroid hormone action.Nucl Recept Signal. 2007 May 17;5:e005. doi: 10.1621/nrs.05005. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007. PMID: 17525795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling-dependent and coordinated regulation of transcription, splicing, and translation resides in a single coregulator, PCBP1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 3;104(14):5866-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701065104. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17389360 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen signaling and the aging brain: context-dependent considerations for postmenopausal hormone therapy.ISRN Endocrinol. 2013 Jul 7;2013:814690. doi: 10.1155/2013/814690. Print 2013. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23936665 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging significance of ER-coregulator PELP1/MNAR in cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2007 Jan;22(1):91-6. doi: 10.14670/HH-22.91. Histol Histopathol. 2007. PMID: 17128415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parker, M. G. (1998) Biochem. Soc. Symp. 63, 45-50. - PubMed
-
- Kushner, P. J., Agard, D. A., Greene, G. L., Scanlan, T. S., Shiau, A. K., Uht, R. M. & Webb, P. (2000) J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 74, 311-317. - PubMed
-
- Onate, S. A., Tsai, S. Y., Tsai, M. J. & O'Malley, B. W. (1995) Science 270, 1354-1357. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., Lin, R. J., Schiltz, R. L., Chakravarti, D., Nash, A., Nagy, L., Privalsky, M. L., Nakatani, Y. & Evans, R. M. (1997) Cell 90, 569-580. - PubMed
-
- Kamei, Y., Xu, L., Heinzel, T., Torchia, J., Kurokawa, R., Gloss, B., Lin, S. C., Heyman, R. A., Rose, D. W., Glass, C. K., et al. (1996) Cell 85, 403-414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

