Proteolytic processing of sapovirus ORF1 polyprotein
- PMID: 15919882
- PMCID: PMC1143638
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7283-7290.2005
Proteolytic processing of sapovirus ORF1 polyprotein
Abstract
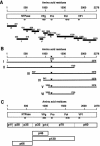
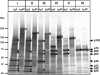
The genome of Sapovirus (SaV), a causative agent of gastroenteritis in humans and swine, contains either two or three open reading frames (ORFs). Functional motifs characteristic to the 2C-like NTPase (NTPase), VPg, 3C-like protease (Pro), 3D-like RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (Pol), and capsid protein (VP1) are encoded in the ORF1 polyprotein, which is afterwards cleaved into the nonstructural and structural proteins. We recently determined the complete genome sequence of a novel human SaV strain, Mc10, which has two ORFs. To investigate the proteolytic cleavage of SaV ORF1 and the function of protease on the cleavage, both full-length and truncated forms of the ORF1 polyprotein either with or without mutation in (1171)Cys to Ala of the GDCG motif were expressed in an in vitro coupled transcription-translation system. The translation products were analyzed directly by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or by immunoprecipitation with region-specific antibodies. The ORF1 polyprotein was processed into at least 10 major proteins: p11, p28, p35, p32, p14, p70, p60, p66, p46, and p120. Seven of these products were arranged in the following order: NH(2)-p11-p28-p35(NTPase)-p32-p14(VPg)-p70(Pro-Pol)-p60(VP1)-COOH. p66, p46 and p120 were precursors of p28-p35 (NTPase), p32-p14 (VPg), and p32-p14 (VPg)-p70 (Pro-Pol), respectively. Mutagenesis in the 3C-like protease motif fully abolished the proteolytic activity. The cleavage map of SaV ORF1 is similar to those of other heretofore known members of the family Caliciviridae, especially to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, a member of the genus Lagovirus.
Figures


References
-
- Belliot, G., S. V. Sosnovtsev, T. Mitra, C. Hammer, M. Garfield, and K. Y. Green. 2003. In vitro proteolytic processing of the MD145 norovirus ORF1 nonstructural polyprotein yields stable precursors and products similar to those detected in calicivirus-infected cells. J. Virol. 77:10957-10974. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blakeney, S. J., A. Cahill, and P. A. Reilly. 2003. Processing of Norwalk virus nonstructural proteins by a 3C-like cysteine proteinase. Virology 308:216-224. - PubMed
-
- Chang, K. O., S. V. Sosnovtsev, G. Belliot, Y. Kim, L. J. Saif, and K. Y. Green. 2004. Bile acids are essential for porcine enteric calicivirus replication in association with down-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:8733-8738. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiba, S., S. Nakata, K. Numata-Kinoshita, and S. Honma. 2000. Sapporo virus: history and recent findings. J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl. 2):S303-S308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

